You can create instances of Records from your code with the
If you need to work with Record instances in your code, be it custom functions, tasks, or your custom application, you can generate Java classes through which you can handle Record instances.
This allows you to decouple the Record instance from its definition better.
Example of difference in coding
RecordHolder record = ctx.getNamespace().createRecord("core::ConstraintViolation");
record.setProperty("message", msg);
ConstraintViolationRecord better = new ConstraintViolationRecord(record);
better.setMessage(msg);
You can then regenerate the classes whenever the Record definition changes.
When you generate Java wrappers for Records, the system creates the following:
- subpage of the target package for every Module
- class for every Record in the respective subpackage
- interface for every Record classes
- RecordWrapperFactoryImpl
- RecordWrapperFactoryImpl for individual modules
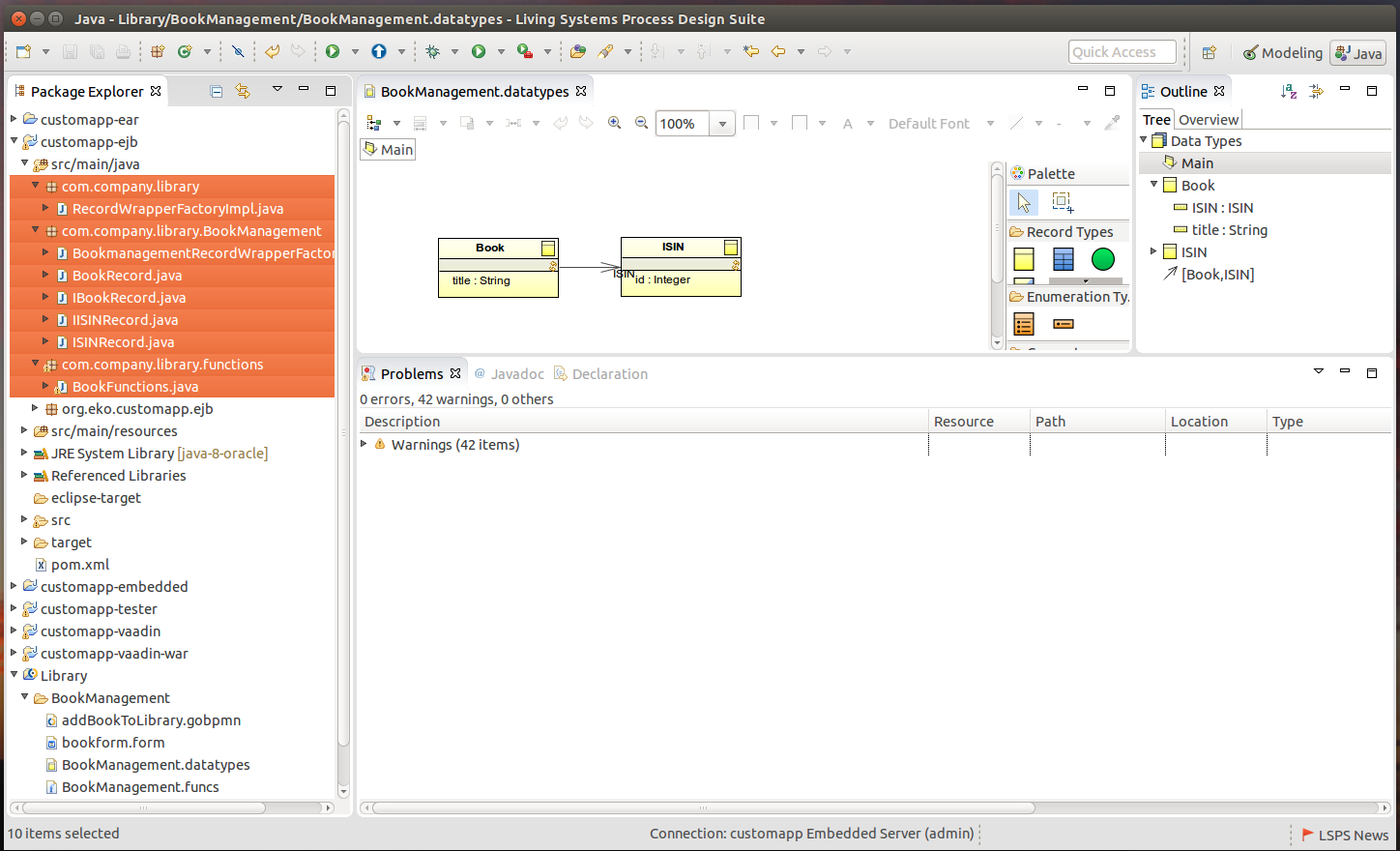
Generated Java Record wrappers
To generate Java classes, do the following:
- Right-click a Module or project and go to Generate > Record Java Sources.
- In the dialog, define the export properties:
- Source folder: path in a project where to place the generated sources
- Package: target package name
- Additional record types: other Records that should be included in the operation (The parameter is primarily intended for including Library Records)
- Class name prefix: prefix of exported class names
- Class name suffix: suffix of exported class names
- Class extends superclass: superclass of the generated Record classes
- Class implements interface: interface of the generated Record classes
- Selected modules: the system generates Java classes for the selected Modules and any dependencies
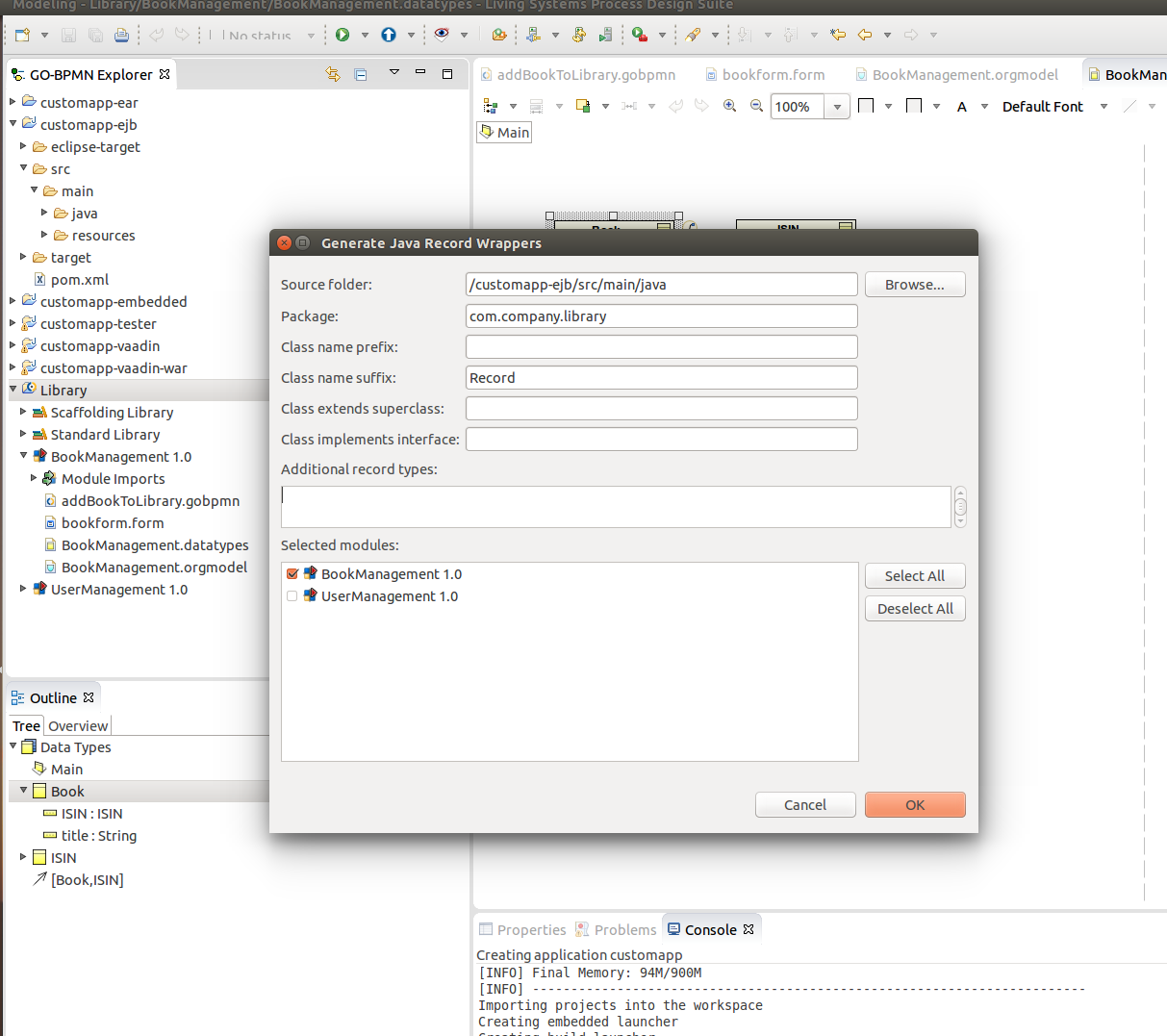
Generating Java Record wrappers
You can use the generated classes in implementation of custom function or task or anywhere in your application code as necessary.
Implementation of a custom function and its definition
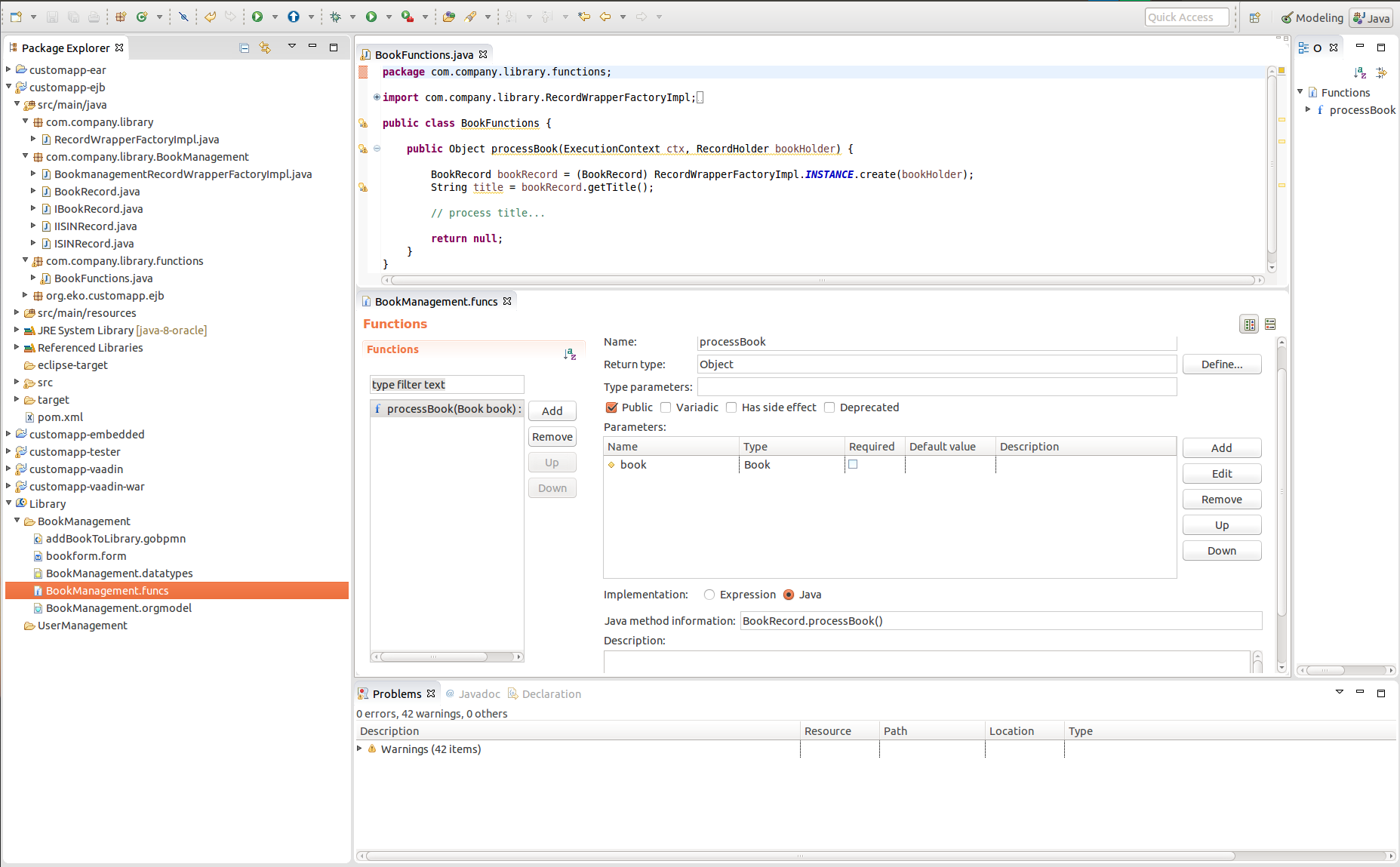
Custom Function implementation and definition
Working with Data Constraints
getConstraints
The getConstaint() function returns a collection of all constraints that are applied to a given record type and properties. These can be potentially null.
executionContext.getProcessModel().getConstraints(recordA, propertyA)
findTag
The findTag() function returns a validation tag with the given qualified name (may be simple or * full).
executionContext.getProcessModel().findTag(qid)



