
This part provides information on how to perform JUnit testing on your models.
Note: This document instructs you to generate the Default
LSPS Applicationand modify the generated sample testing project. The sample testing project is provided for your convenience as part of the Default LSPS Application but you can create your own classes and projects as well. Mind that if you decide to create your own project, you will need to import the jars required by the testing classes, either manually or using maven, create thepom.xmlfile with the test target, and manually create thetest.propertiesfile.
You can create JUnit tests using the API of the following packages:
Important: To be able to use the API of com.whitestein.lsps.test.web and com.whitestein.lsps.test.web.components, purchase the Vaadin TestBench license.
For detailed documentation, refer to the Javadoc documentation in the documentation/apidocs directory in PDS.
Before you work with the testing resources of the LSPS Application, do the following:
-Dcom.whitestein.lsps.vaadin.ui.debug=true property (in PDS, go to Runtime Connection > Runtime Connection Settings; select the connection and click Edit).Note: If you do not want to use the resources generated as part of the Default LSPS Application, you can create them manually: either you import all the dependencies or create a custom pom.xml that will pull them for you. After
mvn clean installand runmvn eclipse:eclipsemake sure to refresh the GO-BPMN Explorer.
To create a JUnit test in the Application User Interface, do the following:
<APPLICATION>-tester project with the sample test classes:SampleNonUIIT.java: a dummy sample test class that uploads a model, creates its instance and evaluates an expression in the context of the Model instanceSampleUIIT.java: a dummy sample test class that tests execution of To-Dostest.properties: relative path to the tested model and to the Standard Library Modulespom.xml: Maven POM file with dependencies Since the tests need a running LSPS server, Maven compilation does not run the tests by default. The pom.xml file therefore defines the lsps.tester parameter, which allows you to run the JUnit tests on compilation: 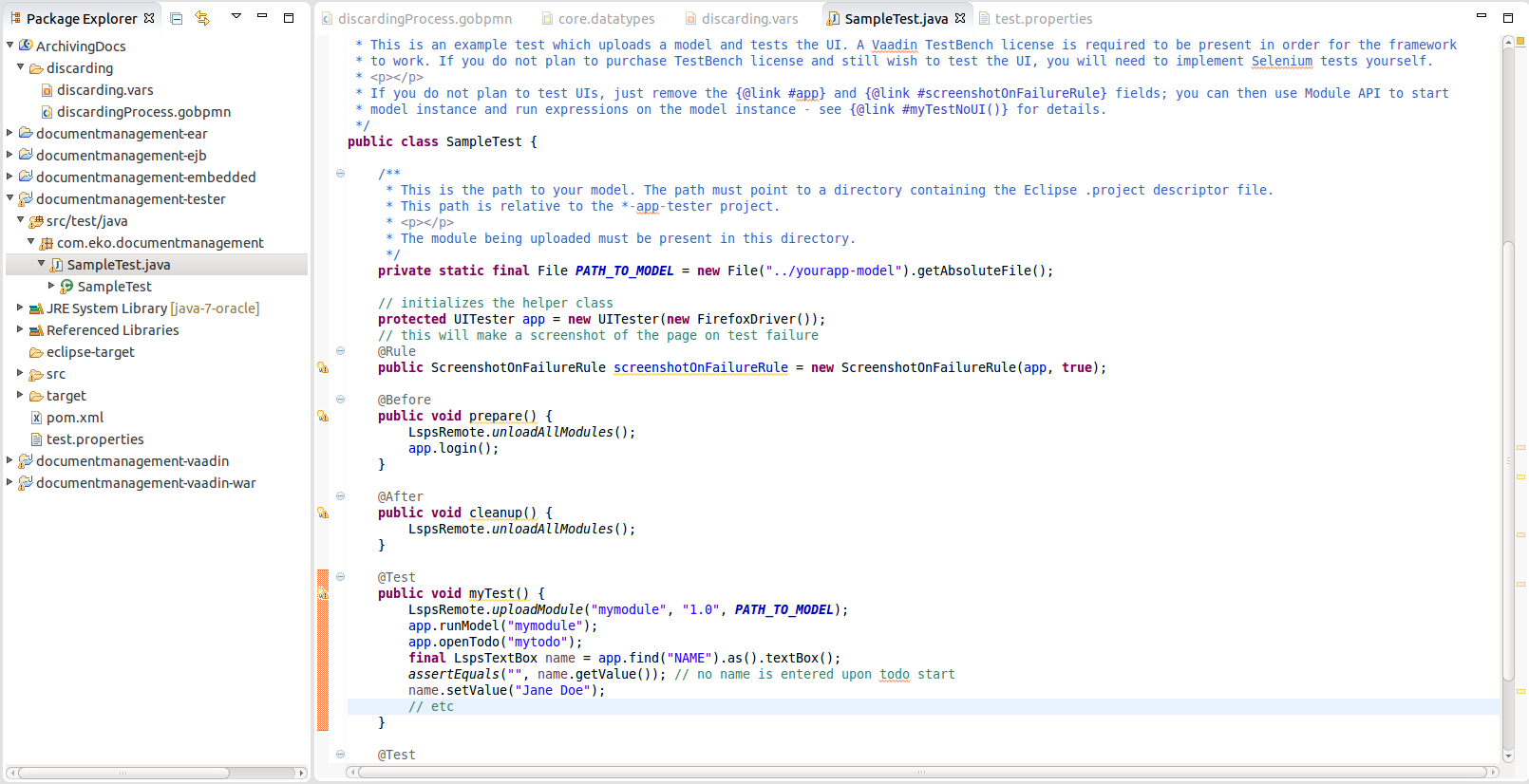
tester project.Expand the src package and open the SampleNonUIIT.java or SampleUIIT.java file. Note that the testing classes are JUnit 4 tests and hence require annotations, such as @Before. The classes provide multiple LSPS-specific testing methods from com.whitestein.lsps.test:
When testing the GUI, you need to create a UITester instance. For tests that do not require GUI testing, you can perform LspsRemote calls.
Edit the sample test file.
From tests, you can access only the model context: Data from child contexts, such as Sub-Process variables, cannot be used for testing.
test.properties file to point to the location with the project with your model if applicable. Optionally, provide paths to libraries.pom.xml file or provided paths to custom libraries in test.properties, open a terminal/command line and go to the location of the test project:mvn eclipse:eclipsemvn clean install.To run your JUnit tests of model, do the following:
mvn eclipse:eclipse) and re-build the maven artifact to acquire the dependencies (run mvn clean install) if necessary.-Dselenium.host=<SERVER_IP> and -Dselenium.port=<SERVER_PORT>. Make sure you enabled the modeling IDs, that is, your server is running with the -Dcom.whitestein.lsps.vaadin.ui.debug=true property.In PDS, right-click the Java test class and click Run As JUnit Test.
Alternatively, on the command line, go to the location of the application tester project and run mvn clean install -Dlsps.tester. Make sure you enabled the modeling IDs, that is, your server is running with the -Dcom.whitestein.lsps.vaadin.ui.debug=true property.