
This section contains instructions on how to provide custom implementation of the LSPS person management modules with custom authorization, authentication, and related operations.
Important: If you want to add authentication against another directory service, such as LDAP and Active Directory, add the respective login module settings to the configuration of your application server (refer to the documentation of your application server). Make sure the users from your directory service exist in LSPS Application (for example, create a cronjob that will synchronize the users).
The default Application User Interface uses its custom person management. The related services are implemented in the pm-exec.jar in the application bundle.
If you want your Custom Application User Interface to authenticate and authorize, you need to provide your implementation of the person management services in a custom pm-<DIRECTORY>-exec.jar file. You can find the source code of an example LDAP implementation here.
To set your application to use a custom directory service, do the following:
pm-<DIRECTORY>-exec ejb project.PersonManagementServiceBean stateless bean that implements the following interfaces:com.whitestein.lsps.os.ejb.PersonManagementServiceLocalcom.whitestein.lsps.os.ejb.PersonManagementServiceRemote (optional)ProcessServiceBean stateless bean that implements the following interfaces:com.whitestein.lsps.os.ejb.PersonServiceLocalcom.whitestein.lsps.os.ejb.PersonServiceRemote (optional)PersonSecurityRoleChangePlugin stateless bean that implements the following interfaces:com.whitestein.lsps.orgstructure.entity.SecurityRoleChangePluginpom.xml of your EAR project, change the dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.whitestein.lsps.person-management</groupId>
<artifactId>lsps-pm-ldap-exec</artifactId>
</dependency>
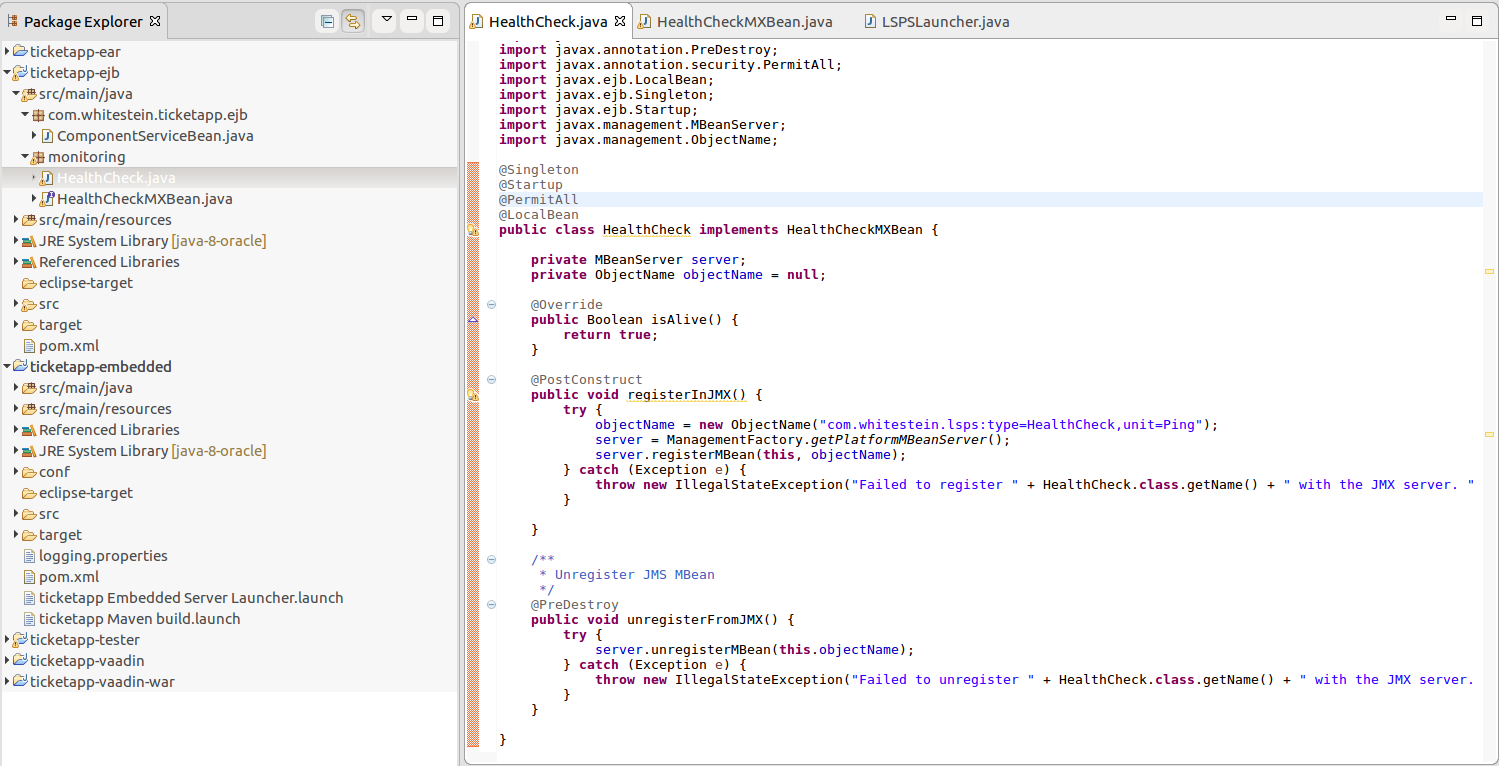
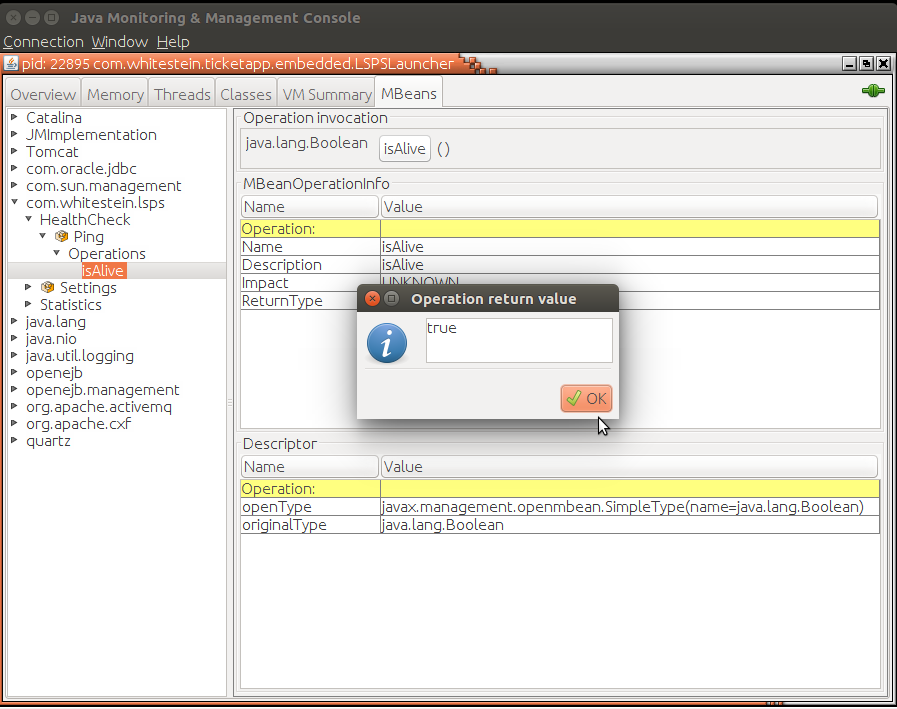
To define an MXBean so its is accessible from JMX monitoring tools, add the interface and the implementation classes to the <YOUR_APP>-ejb project.
To access data from external resources, we will set up connection to the datasource, create an Entity and manage it via an EJB. This will be typically helpful when you have an existing database or your database is populated by an external system, and you want to obtain and manipulate the data from the code of your LSPS Application.
Make sure you have the following ready:
You have set up the data source on the application server with the LSPS application (refer to the application server documentation).
For example, to configure a data source so it is accessible from SDK Embedded Server, in <YOUR_APP>-embedded/conf/conf/openejb.xml, define its data source configuration (You need to restart SDK Embedded Server for the changes to be applied):
...
JdbcUrl jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/./h2/h2;MVCC=TRUE;LOCK_TIMEOUT=60000
Username lsps
Password lsps
# DefaultTransactionIsolation = READ_COMMITTED
</Resource>
<!-- adding this Resource tag:-->
<Resource id="jdbc/USERS_DS" type="javax.sql.DataSource">
JdbcDriver com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
JdbcUrl jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/training_users;
Username root
Password root
</Resource>To work with data from another data source, do the following:
@Entity
@Table(name = "ORDERS_USER")
public class User {
@Id
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "FIRST_NAME")
private String firstName;
public Integer getId() { return id; }
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
}
<YOUR_AP>-ejb/src/main/resources/resources/META-INF/persistence.xml and define the persistence unit with the external data source.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<persistence-unit name="<UNIT_NAME>" transaction-type="JTA">
<provider>org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence</provider>
<jta-data-source><DATASOURCE_ID></jta-data-source>
<mapping-file>META-INF/<PROJECT_NAME>-entities.xml</mapping-file>
<validation-mode>NONE</validation-mode>
<properties>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class" value="org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory" />
<property name="net.sf.ehcache.configurationResourceName" value="META-INF/lsps-ehcache.xml" />
<!-- JBoss specific parameters -->
<property name="jboss.as.jpa.providerModule" value="application" />
<property name="jboss.as.jpa.adapterClass" value="com.whitestein.lsps.common.hibernate.LSPSPersistenceProviderAdaptor" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<entity-mappings xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/orm_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<entity class="org.eko.orderusersapp.entity.User" />
</entity-mappings>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
name="<UNIT_NAME>" updateCheck="false" monitoring="off" dynamicConfig="false">
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory class="com.whitestein.lsps.common.ehcache.JmsCacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"/>
<defaultCache eternal="true" maxElementsInMemory="0" overflowToDisk="false" >
<cacheEventListenerFactory class="com.whitestein.lsps.common.ehcache.JmsCacheReplicatorFactory"/>
</defaultCache>
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.internal.StandardQueryCache" maxBytesLocalHeap="10000000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="false">
<cacheEventListenerFactory class="com.whitestein.lsps.common.ehcache.JmsCacheReplicatorFactory"/>
</cache>
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.spi.UpdateTimestampsCache" maxElementsInMemory="1000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="false">
<cacheEventListenerFactory class="com.whitestein.lsps.common.ehcache.JmsCacheReplicatorFactory"/>
</cache>
</ehcache>
@Stateless
@PermitAll
@Interceptors({ LspsFunctionInterceptor.class })
public class UserBean {
@PersistenceContext(unitName = "user-unit")
private EntityManager em;
public String getUsers(ExecutionContext context) {
User user = em.find(User.class, 1);
System.out.println(user.getFirstName());
return user.getFirstName();
}
}
@EJB
private UserBean userBean;
@Override
protected void registerCustomComponents() {
register(userBean, UserBean.class);
}