
An organization model serves to acquire a group of persons (users) that meet some requirements.
The model defines a hierarchy of organization elements, which group persons, the users of the application. The model can contain the following:
On runtime, a runtime version of the role can be assigned to a person: the person then belongs to the role and any ancestor role or organization unit. A runtime role can define parameters with values. Parameters of any ancestor can be used. If an ancestor has a parameter with the same name as its descendant, the parameter on the descendant is considered the same parameters as the parameter on the ancestor.
To acquire persons in a role or organization unit, call the unit or role as <ROLE_UNIT>(<MAP_OF_PARAMETERS>). You can use the functions in the human module of the Standard Library for additional features.
An organization role groups persons with common behavior, rights, expertise, etc.
One role is usually assigned to multiple persons and one person can have multiple roles. It can be decomposed to other roles and be a target of a decomposition, descendant of a role or organization unit: a person with a role belongs to all ancestor roles and organization units.
Roles can define parameters, which allow you to exclude persons who are in the role or its descendant role but do not have the specified parameter with the specified value.

An organization unit is an umbrella element for roles: A person is part of an organization unit if they belong to a role that is a descendant of the organization unit.
Note that users are added only to roles, not organization units.
It can be decomposed to roles or other organization units and be a target of a decomposition originating from an organization unit: a person with a role belongs to all ancestor roles and organization units.
Organization units can define parameters which allow you to exclude persons who are in a descendant role of the unit but do not have the specified parameter with the specified value.

Note: GO-BPMN uses two decompositions: decompositions in goal structure and decomposition in organization models. The latter is documented below.
Organization units and roles can be decomposed with the decomposition relationship in one or several other organization elements: This enables you to create organization hierarchies and group organization elements; a person who belongs to a role belongs also to all its ancestor roles or role units.
One organization element can be the target or origin of multiple decompositions. However, decompositions cannot create cyclic relationships.
Decomposition can be used between the following organization elements:
Note: The Role-to-Unit decomposition is not supported.
img{Decomposition.png, Decomposition notation, 90px}
When you request persons with a role, it is resolved as follows:
"*", all persons with the role or its descendant roles are returned (role parameters are ignored).When you request persons of an organization unit:
"*", it returns all persons with a descendants of the organization unit (parameters are ignored)Hence, parameters of the role units, organization units and roles provide a filtering mechanism over persons that belong to a role unit.
Example: Consider the following organization model:
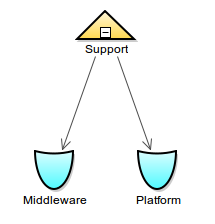 Unit decomposed in two Roles
Unit decomposed in two Roles
- If a task is assigned to the Organization Unit Support (for example,
performers -> {Support([->])}), it is assigned to all persons that have the Middleware or Platform Runtime Roles regardless of their parameter values.- If a task is assigned to the Organization Unit Support with a parameter (for example,
performers -> {Support(["product"->"Wildfly"])}), it is assigned to all persons that have the Middleware or Platform Runtime Roles with no parameter or with the parameterproductset toWildfly.
Example: The role
TechnicalExpertdefines the parameterexpertise.The person Eva is a technical expert without a field of expertise: she is considered an expert in all fields and has the runtime role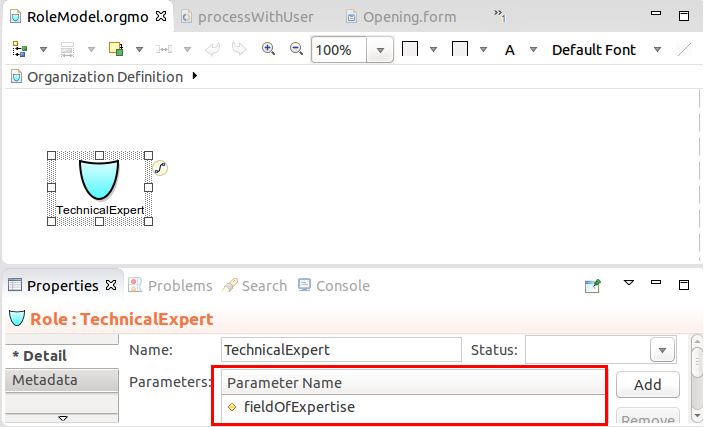 Parametric Role definition
Parametric Role definitionTechnicalExpertwith no parameter.John and James are technical experts specialized in hydraulics and electrics: They have the runtime roles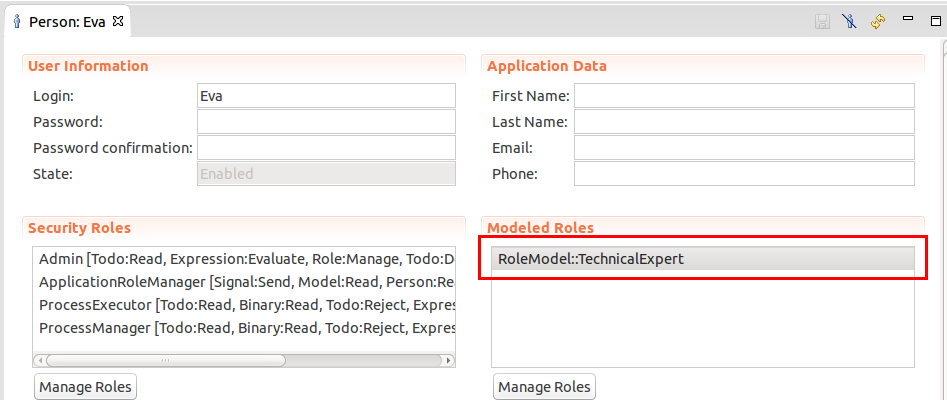 Person view of a person with the runtimee role TechnicalExpert with no parametric value
Person view of a person with the runtimee role TechnicalExpert with no parametric valueTechnicalExpertwith theexpertiseparameter set tohydraulicsandelectrics.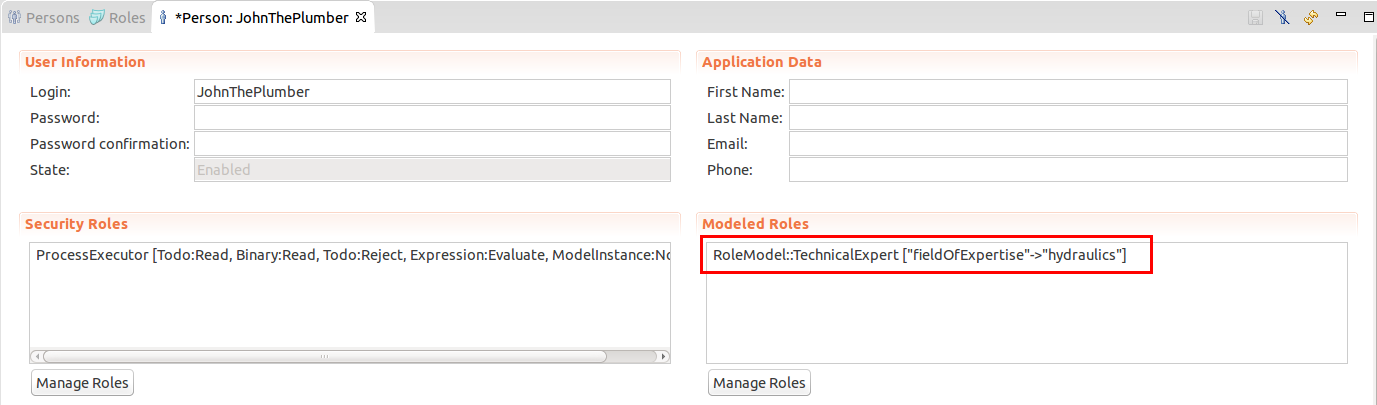 Person view of a person with the runtime role TechnicalExpert with the 'hydralics' expertise parameter
Person view of a person with the runtime role TechnicalExpert with the 'hydralics' expertise parameter
- If a task is assigned to TechnicalExpert([->]), the task is assigned to
- all three persons regardless of the parameter values (any of 'TechnicalExpert' can perform the task);
- If a task is assigned to a
TechnicalExpert("expertise"->"hydraulics", the task is assigned to:
- Eva, the technical expert with no parameter value,
- John, the technical expert with the
hydraulicsparameter value James is left out.
For presentation purposes, you can add the views of the Roles and Unit from other organization definitions to the diagram in your definition as Role and Unit Imports. Note that such imported Role or Unit views cannot be decomposed, however, they can be a target of a Decomposition.
Note: Roles and Unit from other Modules become available for Diagram import only after their Module is imported.