
To debug your models, run LSPS Server in debug mode, add breakpoints to modeling elements in your diagrams and expressions, and run the model on an LSPS Server; both the JVM and the LSPS Server must run in debug mode.
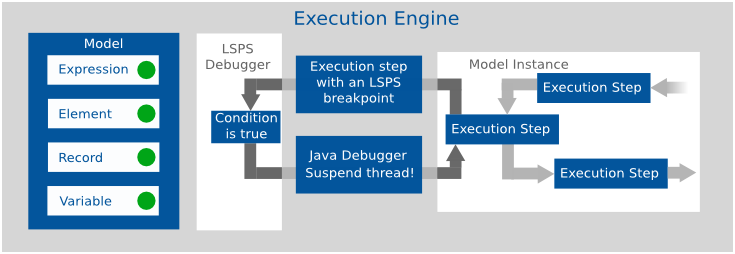
To debug your models, both the Execution Engine and the underlying JVM must run in debug mode. After you start the Execution Engine and JVM in debug mode, you can enable the debug mode in PDS. At that moment, the following happens:
When you then run a model instance in debug mode with LSPS breakpoints on its modeling elements and expressions, and the execution hits a breakpoint, in an execution step, the breakpoint condition is evaluated and if the condition evaluates to true, the LSPS Debugger notifies the Java Debugger to suspend the execution in the execution step.
An execution step is any of the following:
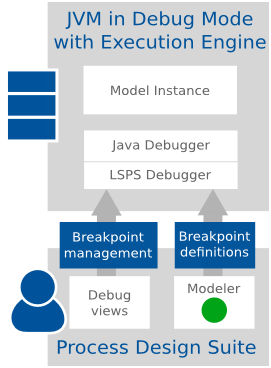
You can connect the LSPS Debugger and debug a model instance that runs on an Execution Engine in a local JVM or on a remote JVM. Generally, you have the following options:
Generally, the connection of the LSPS Debugger to a server, remote or local, is defined in a debug configuration. However, the connection to the PDS Embedded Server is integrated in PDS and it is sufficient to modify the server properties.
To run the PDS Embedded Server in debug mode, do the following:
In the VM Arguments field, add arguments that will run the JVM and the Execution Engine in debug mode:
The -DlspsDebug=true argument runs the Execution Engine in debug mode; the address argument defines the target port: you might provide another port number if required.
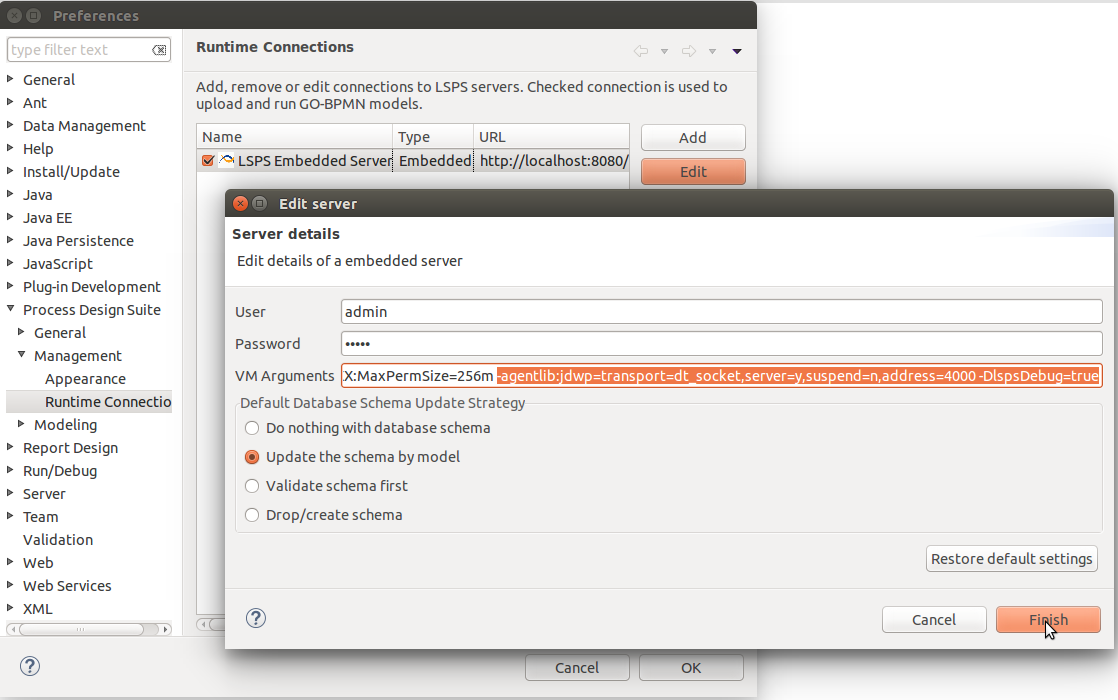
Important: Make sure the user used to establish the connection, in the example it is the admin user, has the security right for debugging: run the server, go to the Management perspective; and in the Person view, check that at least one security role of the Person has the
Debugger:Managepermission.
localhost and port the target port (from the vm arguments above 4000).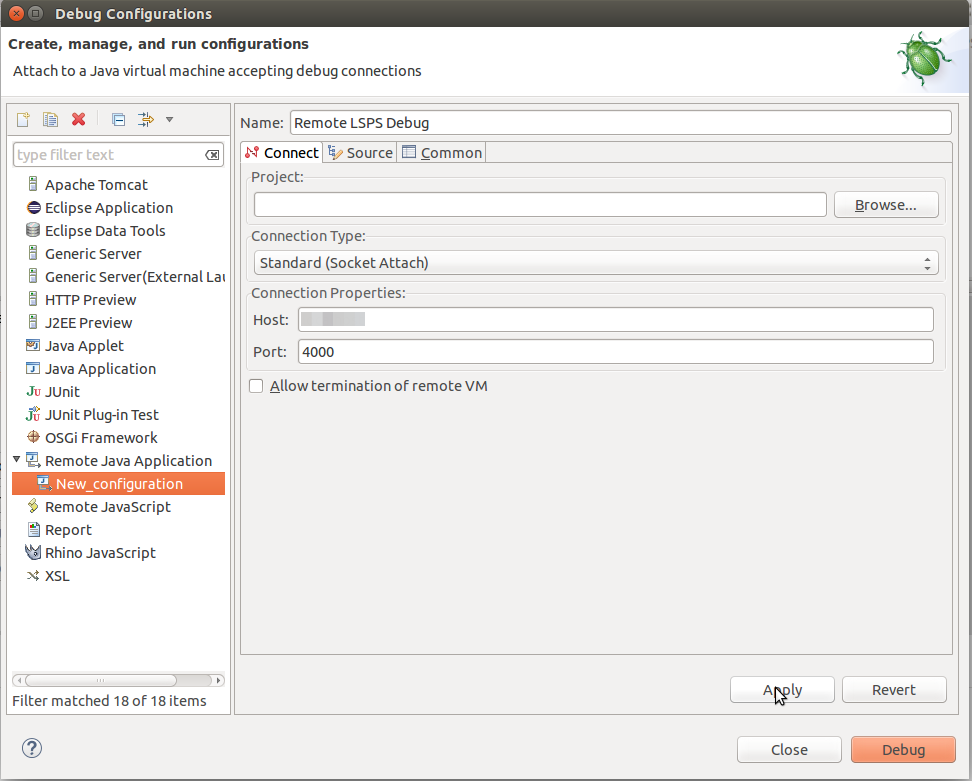
To debug your Custom Application User Interface locally on the SDK Embedded Server, do the following:
MyCustomApp Embedded Server Launcher).-DlspsDebug=true VM argument. 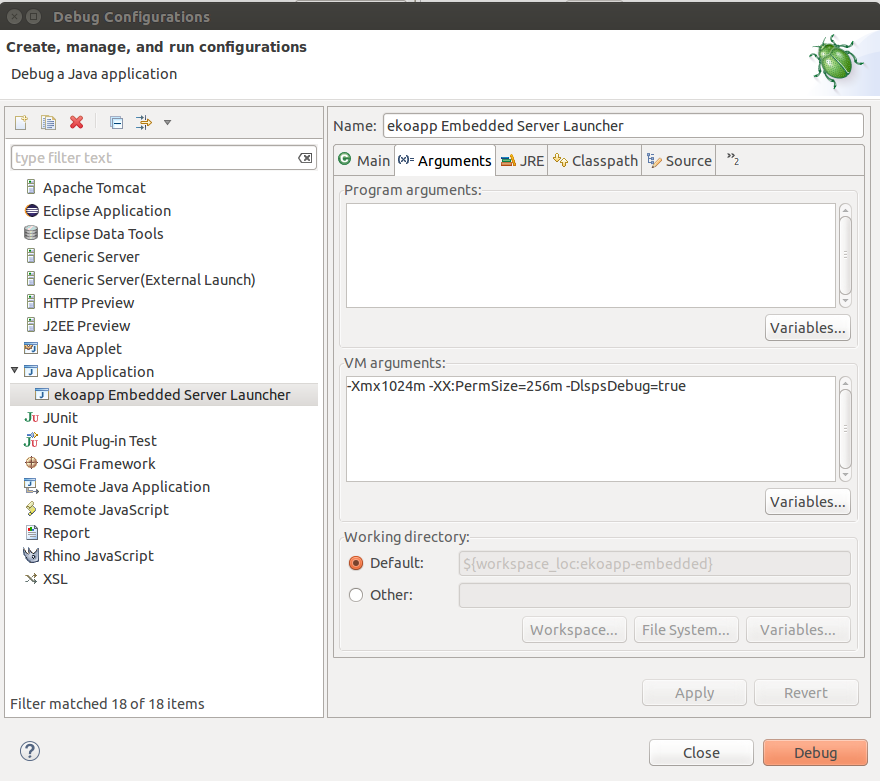
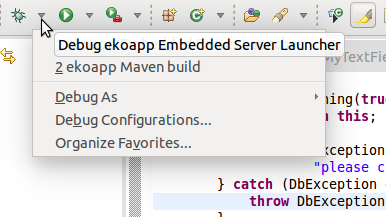
Important: Only one user can connect to the Execution Engine in debug mode since, on connection establishing, any LSPS breakpoints on the server are discarded. If you need to prevent such a scenario, restrict the access of users to the debug feature: remove from persons any security roles with the
Debuggersecurity right.
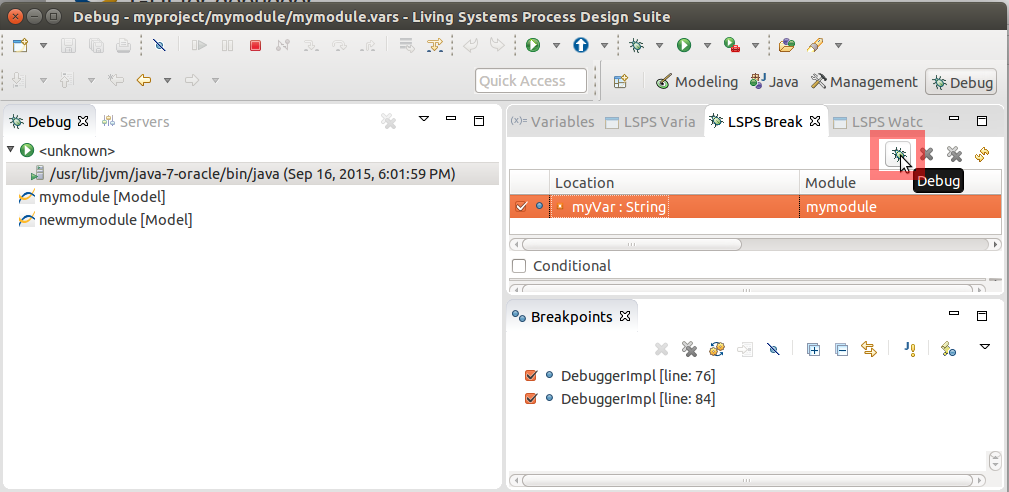
To set up LSPS debugging, do the following:

To start debugging, go to the Debug perspective and click the Debug button in the LSPS Breakpoints to enable the debugging.
When debugging is enabled, the following takes place:

Once you have established connection to the LSPS debugger, and enabled debugging, you can start debugging your model:
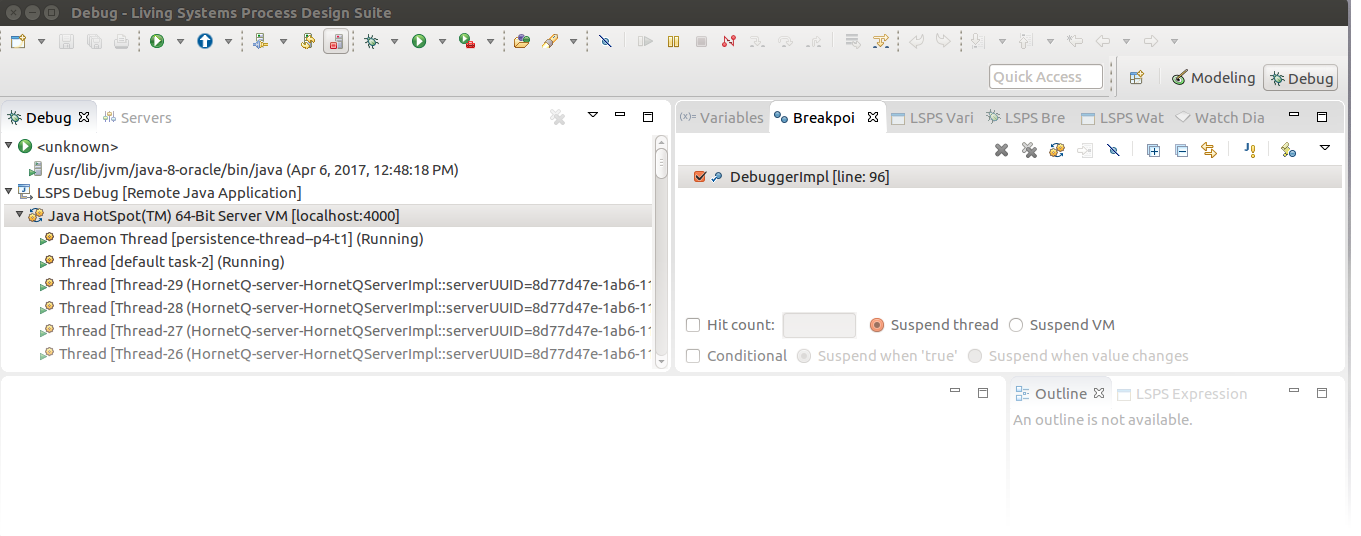
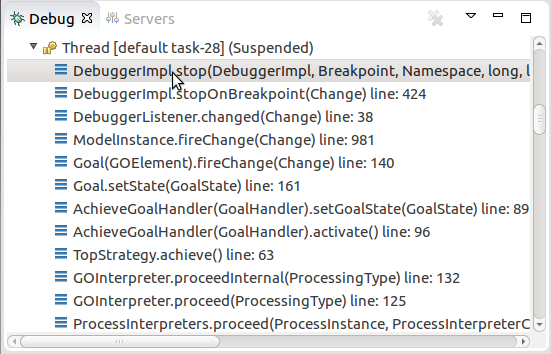
When the model instance hits a breakpoint, the Java thread of the Execution Engine is suspended. Note that the model instance state remains unchanged.
Once suspended, you can examine the model instance in the following views of the Debug perspective:
LSPS Variables: variables from the current execution context
This includes modeling elements and their properties, variables, etc.
To add or remove a breakpoint to an element, do the following:
You can add breakpoints to the following:
Note: Breakpoints on method or function signatures are ignored: if you need to stop at the function or method start, insert the breakpoint on the first expression in its body.
An added breakpoint appears in the LSPS Breakpoints view in the Debug perspective and is displayed as a dot marker in the diagram.
When the breakpoint is triggered, it is visualized either in the Watch Diagram or in the LSPS Expression view, depending on the breakpoint type.
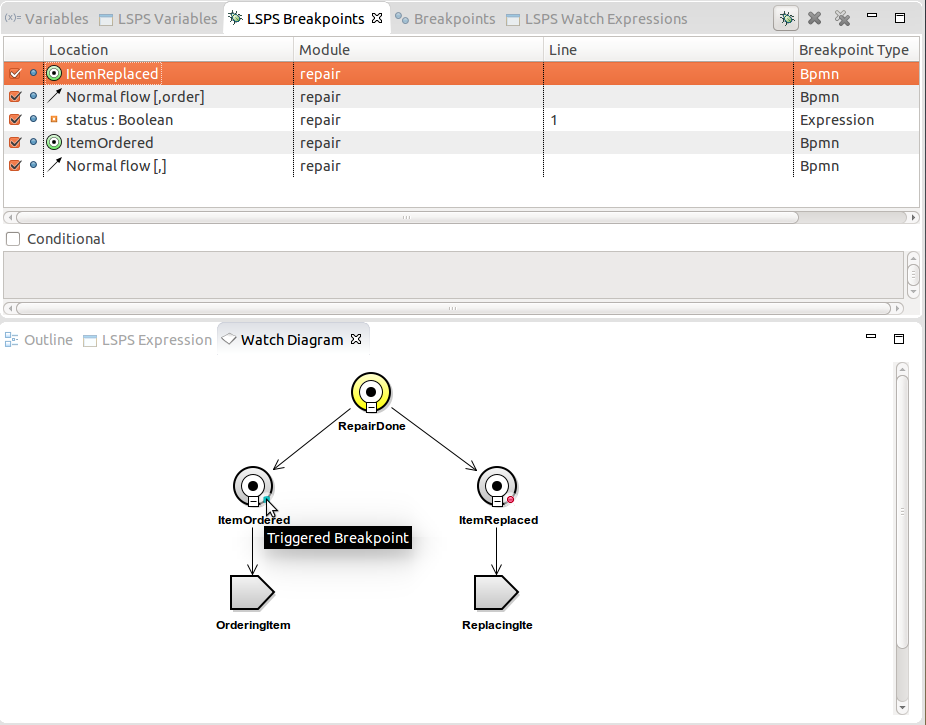
If a breakpoint defines a condition, it is activated only if the condition evaluates to true when the breakpoint is hit.
To add a condition to a breakpoint, select the breakpoint in the LSPS Breakpoints view and define the condition in the Condition area below.
Important: It is not possible to define a breakpoint on a loop with a condition so as to have the breakpoint activated at a certain iteration.
To resume a model instance to the next breakpoint, click the respective button, such as Resume, Step Over, etc., in the LSPS Expressions view.
You can disable and enable LSPS breakpoints as well as define breakpoint conditions in the LSPS Breakpoints view.
Note: Execution Tracker is deprecated. Use the Debugging feature.
To acquire information on runtime data, you can use the Execution Tracker: it provides details about actions during model instance execution; typically you will run tracking only for that part of the model execution you are interested in.
You can enable the Tracker by running the server with the -Dcom.whitestein.lsps.lang.Tracker=true JVM option. To start and stop tracker, go to the Model Management perspective and display the Tracker view (Window > Show View > Other; and in the Tracker View, click the Start Tracking ( ![]() ) button to start execution tracking. Perform the required steps and stop the tracking to display the tracking information.
) button to start execution tracking. Perform the required steps and stop the tracking to display the tracking information.