
You can validate data in your form with the following mechanisms:
Validators: set of expressions that check if values in the form are valid and return a String with an error message if they are not
The String is displayed as an error message either on the current component or the component defined in the Error placement property.
explicitly triggered validation that you can perform from the Handle expressions of your listeners
You will need to collect a set of constraint violations, typically, by calling the validate() function on the respective Record, and then call the showConstraintViolations() function to display the violations in the form. For further information, refer to the documentation on Record validation.
When validating a Record in the Handle expression of a Listener, do the following:
validate() function on the record or property.showConstraintViolations() function to display the error messages of the violation on the respective form components.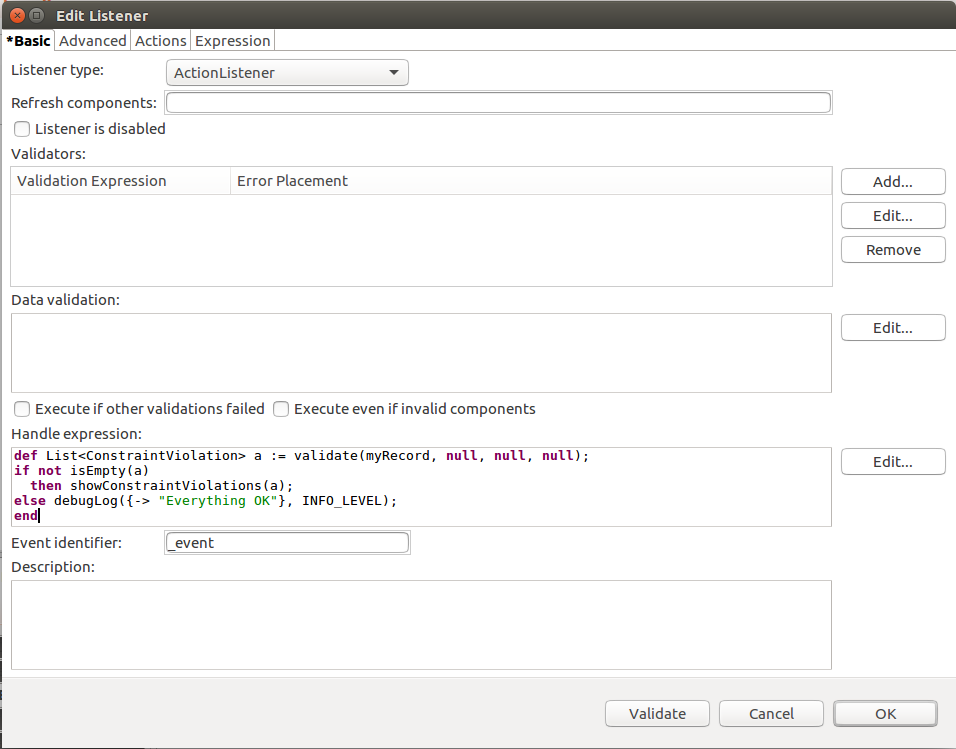
You can define both the validators and the data validation on listeners on their Basic tab:
Validators with validator expressions that return a String when they fail, for example, if searchVar!=null and length(searchVar)>0 then null else “Provide search string!” end.
The String is displayed as an error message either on the current component or the component defined in the Error placement property.
Data Validation as an expression that returns a list of ConstraintViolations: to obtain such a list, use the validate() function.
If you need to display a constraint violation on a particular component, create a constraint violation with record or property set to the same binding as your component; for example, [new ConstraintViolation(payload -> null, record -> selectedRecord, property -> LookupValue.displayName, guid -> null, id -> null, message -> "Incorrect value.")]
The automatic validation passes only if:
null and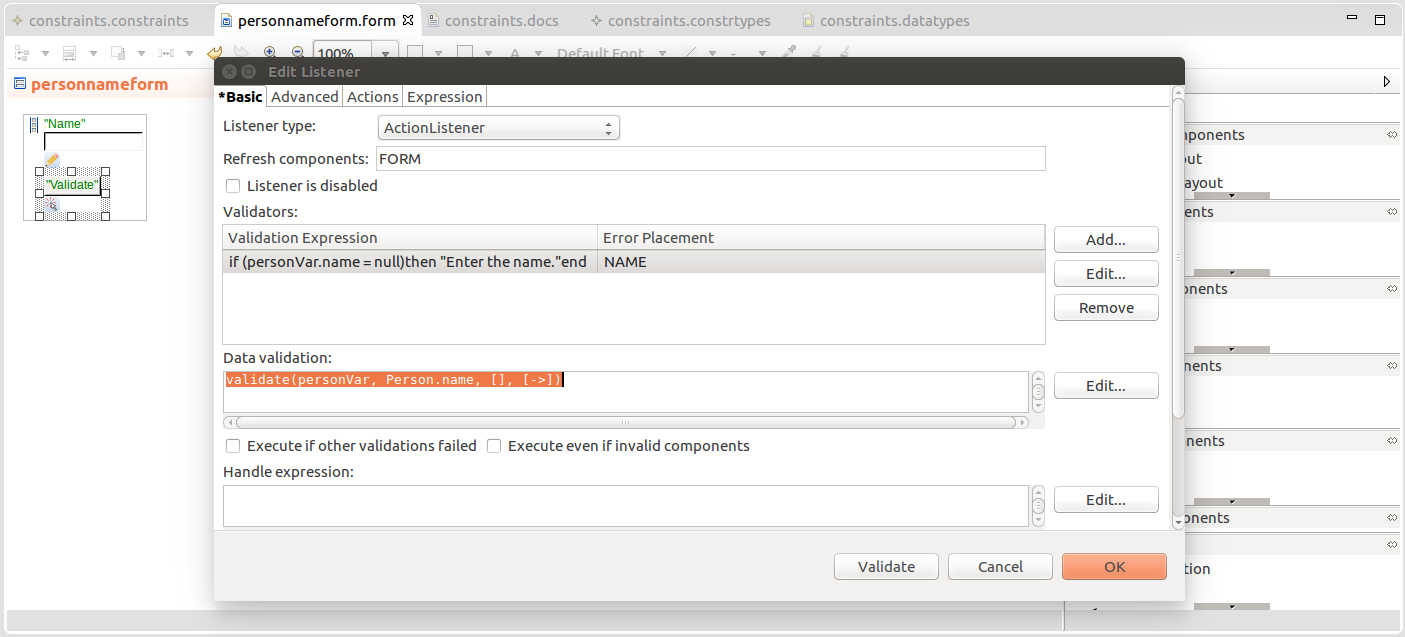
The validation of ValueChangeEvents is governed by their own validation mechanism: they are executed always when their validation passes regardless of other failed validations on other listeners. Also their Execute if other validations failed setting is not taken into account.
In addition, validity of ValueChangeEvents has no impact on the general validity of non-ValueChangeEvents.
Consider the form below: the ISBN text box is in non-immediate mode and its ValueChangeListener defines a validator for the entered text: it must be at least 18 characters long. The Submit button has an ActionListener with the Execute if other validations failed property set to false and executes submit (the Submit property is selected).
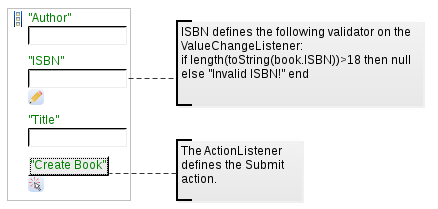
Impact of Listener Validations on their Execution:
| Listener | Listener Type | Listener Validation Outcome | Execute if Other Validations Failed | Executed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Non-ValueChangeEvent | fail | false | no |
| B | Non-ValueChangeEvent | fail | true | no |
| C | Non-ValueChangeEvent | pass | true | yes |
| D | Non-ValueChangeEvent | pass | false | no |
| E | ValueChangeEvent | fail | true | no |
| F | ValueChangeEvent | pass | false | yes |
| G | ValueChangeEvent | fail | false | no |
We assume that the listeners in the table exist in one context:
If necessary, you can force the system to execute a particular listener even after the total validation had failed: Ignoring failed validations on other listeners allows you to perform an action even if the form contains invalid values.
It is then enough that the validation on that particular listener passes for the event to be handled: failed validations on other listeners are ignored.
This behavior is activated by the Execute if other validations failed property of the listener.
When using validation of constraints on form components, by default, validation errors are displayed on the form component that contains the value with the error. However, you can define explicitly additional validation errors displayed on the component or hide such validation errors on the component:
Including validation errors defines additional validation errors displayed on the component.
These could be errors that would otherwise remain hidden. For example, when editing multiple record fields, which would result in an overall record constraint violation, the error for the entire record would not be displayed since there is no form component that references the entire record.
You can define the excluded or included validation errors on the Validation Errors tab of the form component properties.
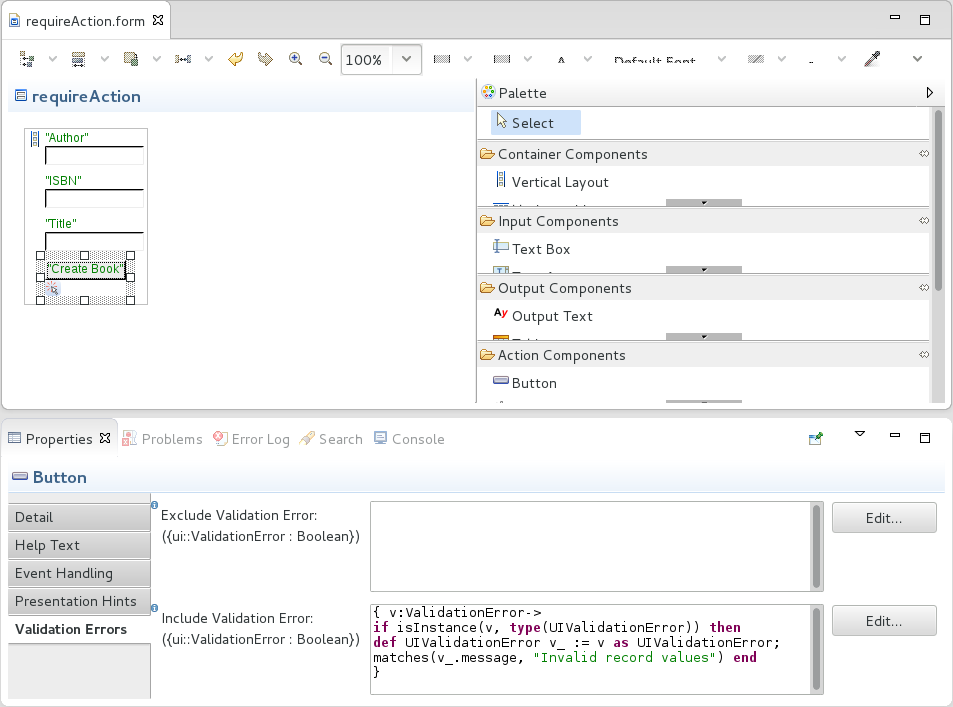
To validate initialized forms, design the forms as follows: