
To check if the values of record properties meet some criteria, use validation with constraints. Constraint validation checks a value of a record property against any constraints defined for the property. Constraints define the conditions the value must meet.
The conditions are defined by the constraint type of the given constraint: The constraint type defines the semantics of the validation—for the constraint to be met, the value of the record or property must meet the condition defined by the constraint type.
You can check if a value of a record property meets the underlying constraints by calling the validate() function. The call returns a list of violations with information on which field violates the given constraint and a violation message.
You can check the constraints defined either for a property or for the entire record:
To provide additional granularity to validation on runtime, validation can pass tags to refine the validation.
def Book b := new Book(isbn -> "123");
validate(record -> b, property -> Book.isbn, tags -> {onCreate(),stock()}, context -> null)
//returns a list with the constraint violations of the isbn value
//that have the tag onCreate or stockInstead of tags, the validate() call can pass the context parameter, which is an object of type Map<String, Object> (either context or tags can be passed).
Note: When validating record data that is displayed in a form component (it is bound to the form component), you can display violation messages in the form with the
showDataErrorMessages()function and from a ui::form with theshowConstraintViolations()function.
A constraint defines what value of a record field or property is allowed.
It is defined for a record field and is of a particular constraint type. The constraint type defines the semantics of the validation—for the constraint to be met, the value of the Record or property must meet the condition defined in the constraint type.
For details on constraints and their properties, refer to the Modeling Language Guide
To define a constraint for a Record or a Property, do the following:
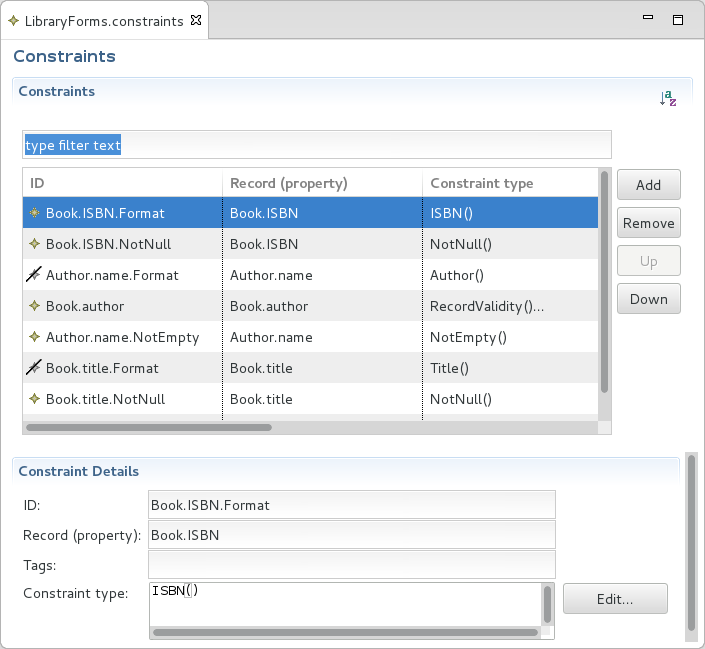
validate() on the record or property instances.Note: The Standard Library contains an extensive set of constraint types. Hence check the available constraint types before defining custom constraint types.
To define a constraint type, do the following:
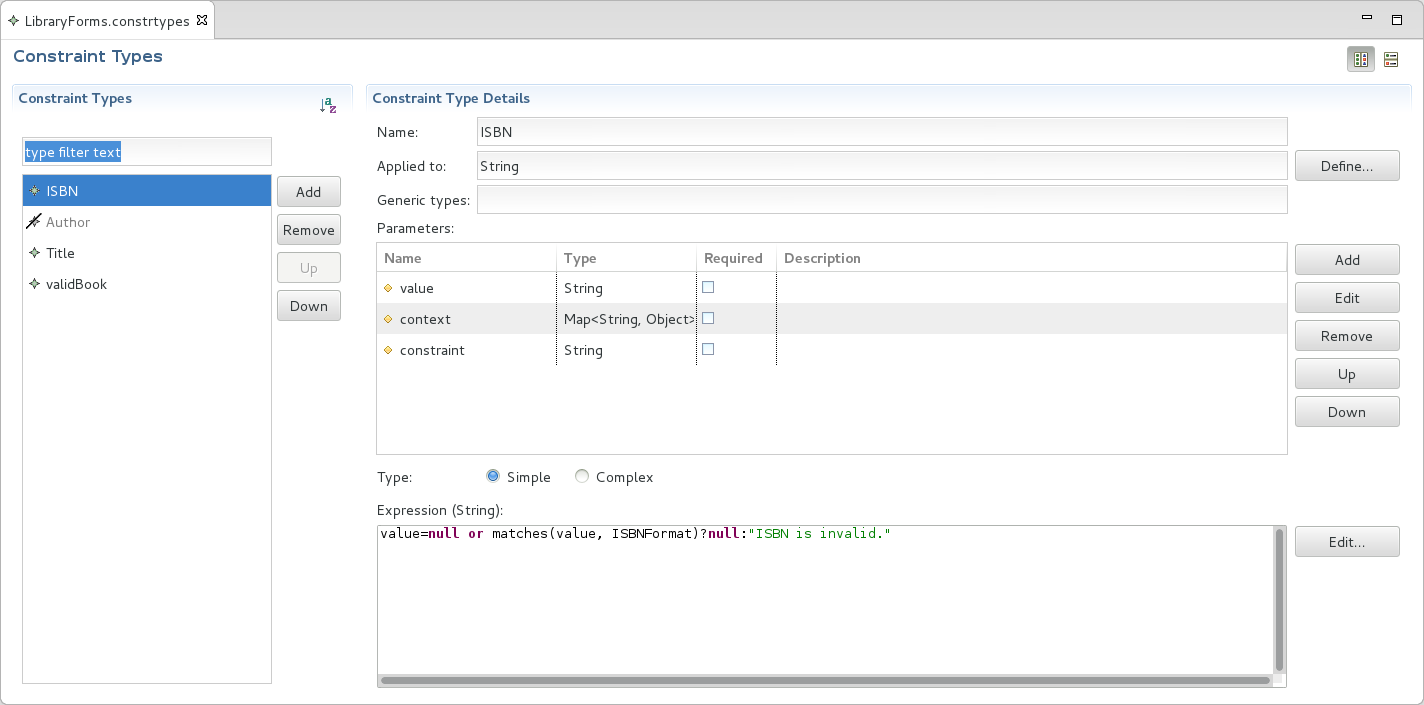
Typically tags define the stages at which the constraint should apply, such as, create or update so that a constraint is applied only if the has one of the tags required by validation.
Note that constraints that do not define any tags are checked always when their record or property is validated.
def Book b := new Book(title -> null, isbn -> "123");
b.title := "1984";
//will return constraint violation defined for any of the book fields
//that have a tag list that includes the update or create tag:
validate(b, null, {update(), create()}, null)
To define a tag, do the following: