
LSPS Documentation
Note: This tutorial uses the
formsmodule as its form implementation.
Required outcome: A form with a grid and table that use a custom data source and support filtering.
Note: You can download the tutorial model here: once you have imported the archive, you can test the model by running the filterGrid module.
forms::DataSource interface.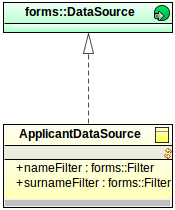
Adapt the data source methods so that the getCount() and getData() methods handle the filtering.
The filters are passed as input parameters to the methods.
Example data source methods
ApplicantDataSource {
public Integer getCount(Collection<forms::Filter> filters){
def String firstnameFilterSubstring := getFilterValue("firstName", filters);
def String surnameFilterSubstring := getFilterValue("surname", filters);
//count query that filters the results:
getApplicants_count(firstnameFilterSubstring, surnameFilterSubstring);
}
public List<Object> getData(Integer startIndex*, Integer count*, Collection<forms::Filter> filters, Set<Sort> sortSpecs){
def String firstnameFilterSubstring := getFilterValue("firstName", filters);
def String surnameFilterSubstring := getFilterValue("surname", filters);
//query that gets results and applies filters:
getApplicants(firstnameFilterSubstring, surnameFilterSubstring);
}
private String getFilterValue (String filterParameterName, Collection<forms::Filter> filters){
//get first filter with matching name:
def forms::Filter firstMatchingFilter := getFirst(filters, { f -> f.id == filterParameterName});
// get search substring in filters:
def String filterSubstring := firstMatchingFilter == null ? null : (firstMatchingFilter as SubstringFilter).value;
filterSubstring
}
public Boolean supportsFilter(forms::Filter filter*){
if
filter.id == "firstName" || filter.id == "surname" then true;
else
false
end
}
public Boolean supportsSort(Sort sort*){
false
}
public String toString() {
#"ApplicantDataSource"
}
}
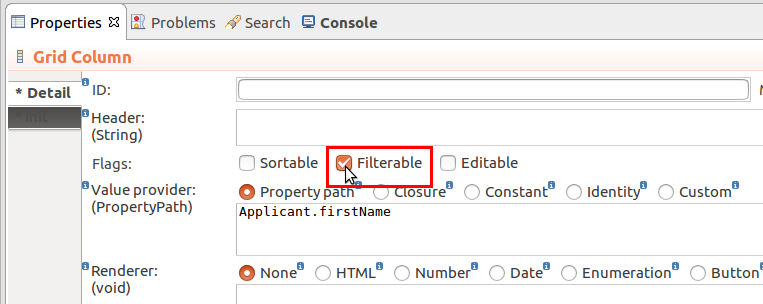
c.setFilterConfig(new FilterConfig(filterId -> "FILTERNAME")).new FilterConfig(filterId -> "FILTERNAME").