
The LSPS Application build is a standard maven build and as such you can manage all its dependencies.
Also, you can expand it to create zip files with your modules and migration tool with database-migration scripts.
Once you have adapted the build, you can test it on SDK Embedded Server. For deployment to other servers, build the application EAR.
To simplify the deployment during development of the LSPS Application, the SDK comes with SDK Embedded Server and its launcher: the launcher is created when you generate the LSPS Application along with the Maven build configuration for the application build. The launcher runs SDK Embedded Server with an exploded deployment of your application on its classpath: The configuration runs the main() method in the <APP_PACKAGE>.embedded.LSPSLauncher class.
Important: SDK Embedded Server is yet another server that runs locally just like Designer Embedded Server.
You can run the server with the application in normal or debug mode:
Hence to build your application and run it on SDK Embedded Server, do the following:
<YOUR_APP>-embedded project and select Run As > <YOUR_APP> Maven Build. 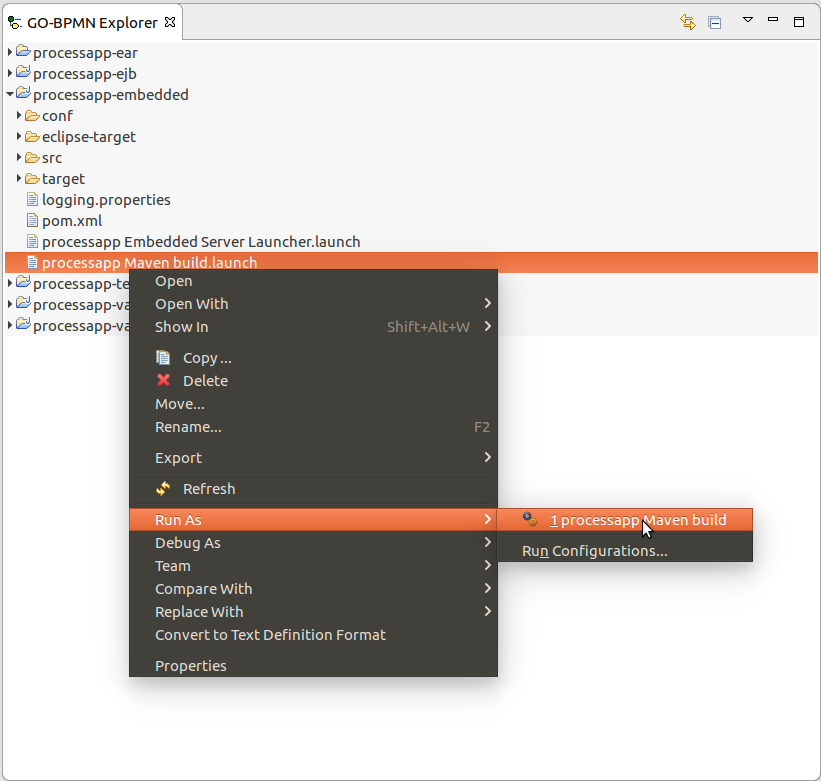
Note: Next time build the application from the Run menu or from the drop-down of the Run icon
on the toolbar.
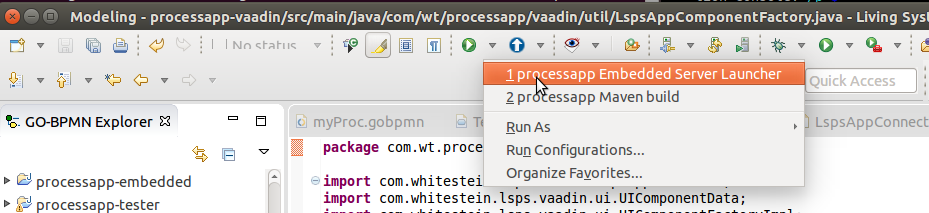
<YOUR_APP>-embedded project and select Run As > <YOUR_APP> Embedded Server Launcher. Note: Next time run the application server from the Run menu or from the drop-down of the Run icon
on the toolbar.
To build the application EAR so you can deploy it on a supported application server, run mvn clean install in the directory with the root pom.xml. Consider running the build with the provided tests with mvn clean install -Dlsps.tester. The tester package includes various checks, including a check of the ear content against the dependencies in the jboss-deployment-structure.xml.
Important: When preparing LSPS Application EAR for production environment, disable the form preview feature from the application: Create a custom application navigator class that extends DefaultAppNavigator and override its addAllViews() method:
public class AppAppNavigator extends DefaultAppNavigator { public AppAppNavigator(UI ui, ViewDisplay display) { super(ui, display); } @Override protected void addAllViews() { addView(todoListViewId(), todoListViewClass()); addView(documentsViewId(), documentsViewClass()); addView(runModelViewId(), runModelViewClass()); addView(appSettingsViewId(), appSettingsViewClass()); addView(todoViewId(), todoViewClass()); addView(documentViewId(), documentViewClass()); //remove this: //addView(formPreviewId(), formPreviewViewClass()); } }Make your LspsUI class (typically AppLspsUI), use this navigator: override the createNavigator method:
@Override protected void createNavigator(ViewDisplay display) { Navigator navigator = new AppAppNavigator(getUI(), display); navigator.addViewChangeListener(new PageTitleFromAppView()); }
The output EAR file is located in the target directory. To deploy follow the deployment instructions for your server.
To export a module into a deployable zip file as part of your Maven build use ModelExporter: ModelExporter exports the module with all imported modules and their dependencies including the Standard Library Modules.
To integrate the export in your Maven build include the plug-in in your pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>java</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.whitestein.lsps.export.ModelExporter</mainClass>
<arguments>
<argument>d:\CustomerModule</argument>
<argument>processes\Main</argument>
<argument>d:\CustomerProject\target\stdlib</argument>
<argument>d:\result.zip</argument>
</arguments>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Your can then use the resulting zip file as input for the uploadModel in your pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>uploadModel</id>
<goals>
<goal>java</goal>
</goals>
<phase>deploy</phase>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.whitestein.lsps.mconsolecl.Main</mainClass>
<arguments>
<argument>modelUpload</argument>
<argument>-h</argument>
<argument>${modelUpload.host}</argument>
<argument>-u</argument>
<argument>${modelUpload.user}</argument>
<argument>-p</argument>
<argument>${modelUpload.password}</argument>
<!-- The output file of the ModelExporter run:-->
<argument>-m</argument>
<argument>d:\result.zip</argument>
<argument>--dbUpdateStrategy</argument>
<argument>${modelUpload.dbUpdateStrategy}</argument>
</arguments>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
To generate a tool for migration of your business database as part of the build, do the following:
<YOUR_APP>-db-migration in your application directory and add it to modules of the root pom.xml: mvn archetype:generate -DgroupId=<YOUR_APP_PACKAGE> -DartifactId=<YOUR_APP>-db-migration -DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart -DinteractiveMode=falsecom.whitestein.lsps.db-migration, artifact Id to <YOUR_APP>-db-migrationand packaging to jar.src/main/scripts and the mainClass property set to <YOUR_APP_PACKAGE>.db.migration.<YOUR_APP_NAME>DbMigrationfilters configuration. mvn clean install eclipse:eclipse.mkdir -p src/main/scripts/db/migration/mysql.<YOU_APP>.db.migration and set the schema table name. import com.whitestein.lsps.dbmigration.DbMigration;
public class MyBusinessDataMigration extends DbMigration {
//define the name of the schema version table:
private static final String SCHEMA_VERSION_TABLE = "SCHEMA_VERSION_TABLE";
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyBusinessDataMigration().migrate(args);
}
protected String getSchemaVersionTableName() {
return SCHEMA_VERSION_TABLE;
}
}
Add migration scripts to the resources directory, in the example src/main/scripts/db/migration/mysql: make sure the names of the scripts follow the convention <DB_TYPE>_V<VERSION>_<SCRIPT_NO>__<COMMENT>.sql, for example, MYSQL_V1_0__Initialize.sql.
DB_TYPE values can be H2, DB2, ORACLE, SQLSERVER, or MYSQL
When creating migration scripts for your model data, consider generate update scripts and modify these as required.
Example pom.xml for the db-migration tool
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>sk.eko</groupId>
<artifactId>pa</artifactId>
<version>0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.whitestein.lsps.db-migration</groupId>
<artifactId>pa-db-migration</artifactId>
<name>Pa: Database Migration</name>
<description>Pa: Database Migration</description>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.whitestein.lsps.db-migration</groupId>
<artifactId>lsps-db-migration</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/scripts</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<filters>
<filter>
<artifact>*:*</artifact>
<excludes>
<exclude>META-INF/*.SF</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.DSA</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.RSA</exclude>
</excludes>
</filter>
</filters>
<outputFile>${basedir}/target/${project.artifactId}-${project.version}-full.jar</outputFile>
<transformers>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer">
<mainClass>sk.eko.pa.PaDBMigration</mainClass>
</transformer>
</transformers>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skipTests>true</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>migration.tests</id>
<activation>
<property>
<name>migration.tests</name>
</property>
</activation>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skipTests>false</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
</profiles>
</project>
If you plan to use libraries that are not imported by default, add them to the application pom.xml as dependencies, so they are included by maven automatically, and compile the application:
<dependencyManagement> of the main pom.xml.mvn clean eclipse:clean eclipse:eclipse install lsps:updateClasspath -DskipTests.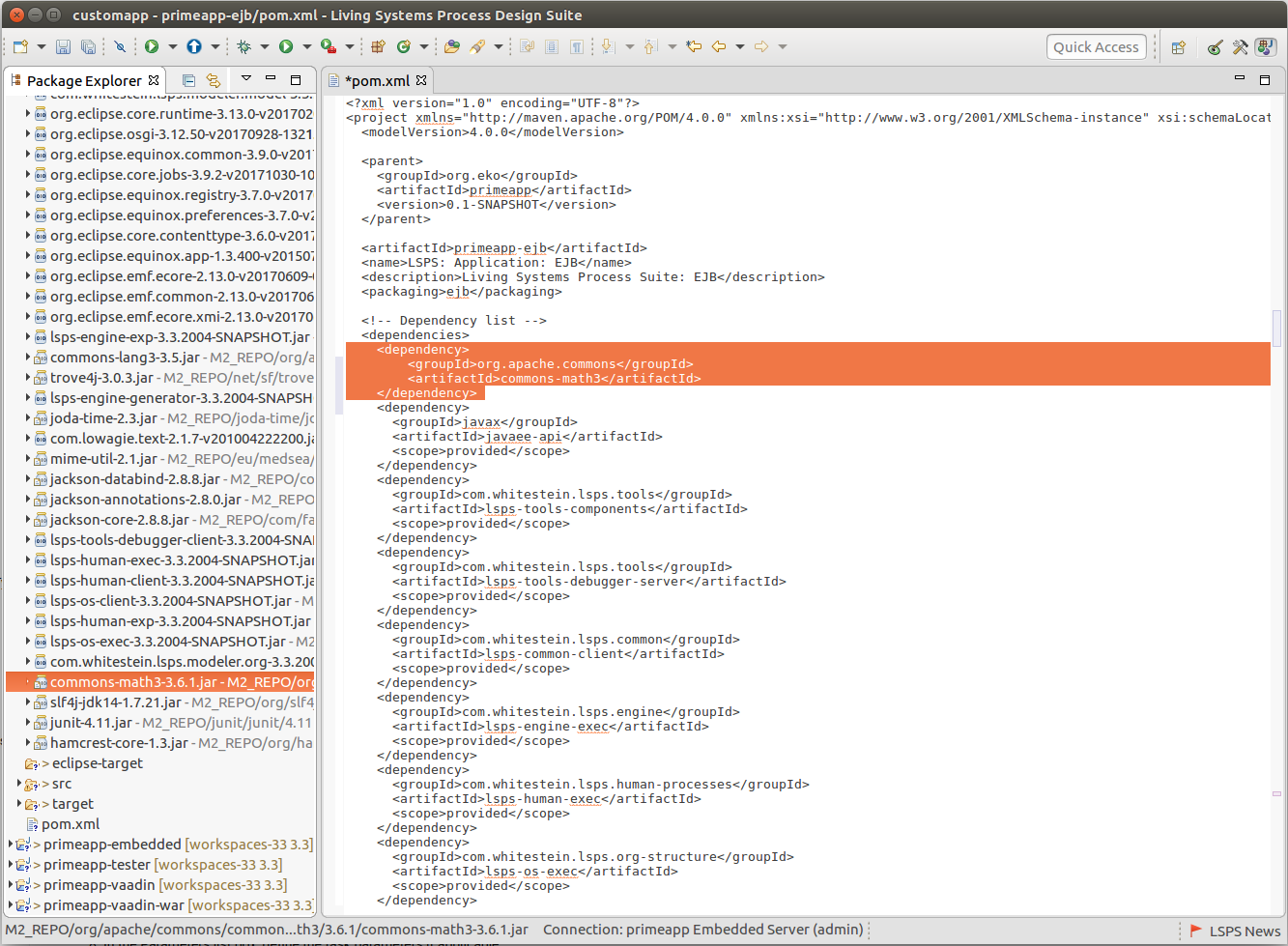
To remove a webapp you do not need, such as Monitoring, from dependencies, do the following:
LSPSLauncher class in the embedded project.