
All forms allow you to perform the following actions:
To execute some logic, before or after the component tree of your form is initialized (to create a pre-init or post-init hook), add the required code to the preCreateWidget() or postCreateWidget() method in the methods file of the form.
Example content of the MyTable.methods file with methods for MyTable.form
MyTable {
private void preCreateWidget() {
//running an asynchronous model instance that will notify
//the respective users about that somebody opened the document and
//is about to edit it:
createModelInstance(false, getModel("notifications"), null);
}
private void postCreateWidget() {
//get a list of form components of the hl layout component:
componentList := hl.getComponents();
//sets the value of a label to display the list of components:
compListLabel.setValue(toString(componentList));
//display a popup on form load:
createMyPopup().show();
}
}To detect geoposition of the device in your form, use the Forms.detectLocation() method.
The instructions for the client browser on how to provide the geographical position data is defined by the PositionOptions object that can be passed as parameter:
false)timeout: time in milliseconds that can pass before the call fails
On such failure, the call returns GeolocatorError.Timeout. The countdown starts when the user permits the detection. By default, no timeout is applied.
maximumAge: maximum accepted age of a cached position
The default value is 0, so that cached positions are not accepted.
If no PositionOptions is passed the default values are applied.
Example detectLocation() call
Forms.detectLocation(
new forms::PositionOptions(
enableHighAccuracy -> true,
timeout -> 10000,
maximumAge -> 1000), { ge ->
forms::notify( caption-> "This is the position: "+ ge.position + " error: " + ge.failure)
}
);To get the current size of the browser window in DIPs, run the Forms.getBrowserWindowSize() method.
When editing a shared record in forms, the changes are applied instantly: when you change the value in a text field that is bound to a record property, the change is persisted when the field loses focus. Generally this is not the required behavior: you want to apply changes only on submit or when some other confirming action takes place.
To implement such a behavior, use proxies of your record in forms.
Important: Proxy objects are not supported by forms created with the ui Module: these forms use execution levels created with the (../ui-vaadin/uispecialcomponents.html::viewmodel) component to isolate any changes instead.
When designing forms that make use of change proxies, consider creating and merging objects out of your form definition: This will keep your form definition easier to maintain and reuse since it will hold only presentation logic. You can do so by defining a parametric constructor that will take the logic-related arguments, such as, change proxies, and action handlers.
For examples, refer to Creating a Modal Popup and Creating a Public Popup.
To save the Document or To-Do with your Form, call Forms.save(): the state of the Document or To-do will be saved as the internal state of the Document or To-do as part of its model instance. The method returns the shared record instances human::SavedDocument or human::Todo depending on whether it was created in a document or in a todo respectively. As part of the save action the form component tree is garbage collected by the LSPS garbage collector to prevent too big a component trees from being saved.
Note that while Saved To-dos remain accessible to the user even after they navigate away from the To-do page, you will probably need to provide a way how to access saved Documents: for example, you could create another document with a form that will contain a list of available saved Documents. Saved Documents can be accessed via the SavedDocuments shared record.
Important: The save action fails if the user attempts to save a Popup state.
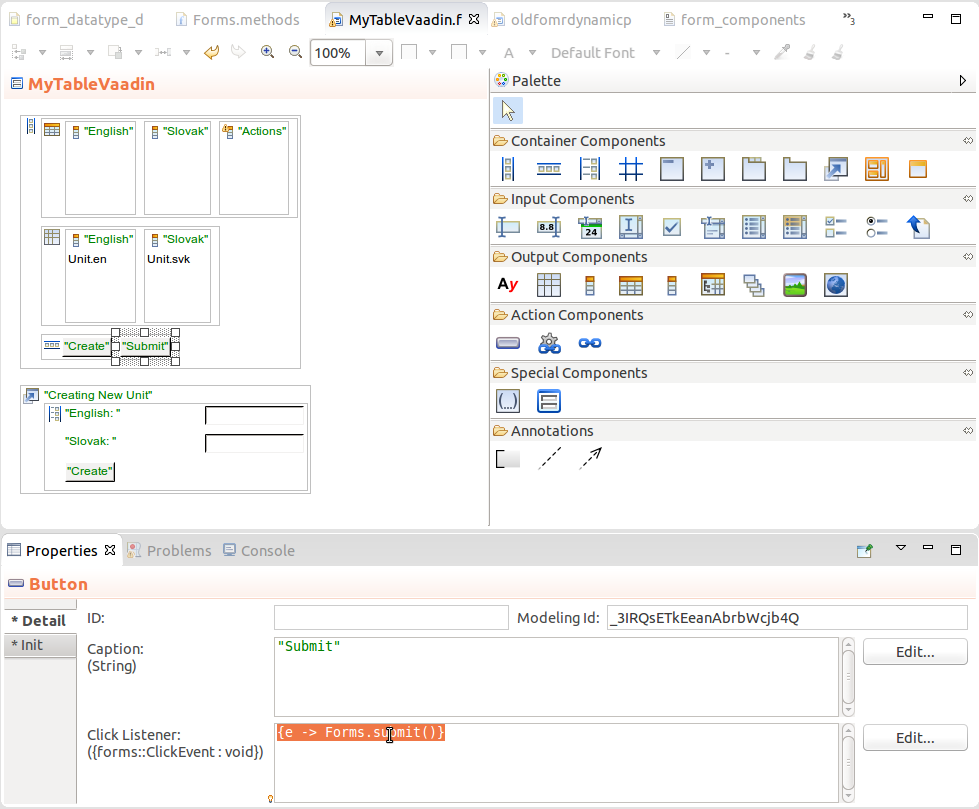
To submit a to-do or document, call the static Forms.submit() method. Typically you will do so on button click: insert a Button component into the form and in its Details in the Properties view define the call in the Click Listener property:
{e -> Forms.submit()}
The method can define a Navigation parameter: on submit the form will navigate to this location:
{e -> if myForm.isValid() then Forms.submit(new UrlNavigation(url -> "www.lezecka-akademia.sk")) end }
Important: If the underlying User Task or Document defines a Navigation parameter, the submit() Navigation is ignored. If neither the User Task or Document or the submit() call define a Navigation, the system navigates to the To-do List or your home page.
To navigate from a form, use one of the navigate methods of the Forms record:
def Button navigateButton := new Button("Navigate", {e -> Forms.navigateTo(new UrlNavigation(url -> "http://sme.sk"))});
//button that navigates to a new document that has a Navigation Factory function:
def Button navigateToDocumentButton := new Button("Navigate", {e -> Forms.submit(); Forms.navigateTo(getMyForm(12))});
On navigation, the current transaction is committed: if you are performing any action after the call, these will take place in a new transaction.
Note that navigation on submit for Documents can be defined directly on the Document definition as well.