
An Event is any element in a BPMN-based Process or Plan model that triggers or terminates the workflow, thus modifying the execution pace or causing a flow change.
Based on the position and function in the workflow, the following types events are available:
A Start Event indicates where a particular workflow starts. When triggered, it creates the context for the element, that is, a process, plan, or subprocess, and produces a token, which leaves through its outgoing flow, in the context.
A Start Event has no incoming flow and only one outgoing Normal Flow.
In Plans of Goal-based Processes and Sub-Processes, its None Start Event is triggered when the Plan becomes running. A Plan can contain only a None Start Event.
While a model instance is running, any Start Events in its BPMN-based Process can create their process instance when their trigger occurs: if there is a Condition Start Event and its condition is true, the event is triggered when the model instance starts and whenever the condition becomes false and true again as long as the model instance is running.
Start Events with triggers can start BPMN-based processes and inline event sub-processes:
A None Start Event is triggered when its parent context is created. It does the following depending on its location:

A Conditional Start Event defines a boolean condition expression as its trigger and starts a BPMN-based Process or an inline-event subprocess:
Note that the condition cannot reference local context since the context does not exist at the moment when it is evaluated.

A Signal Start Event creates the context of a BPMN-based Process or an inline-event subprocess and produces a token when it receives a Signal that passes through the Filter.

A Timer Start Event instantiates a BPMN-based process or an inline event subprocess at a particular point in time. The point in time is defined by its date and period attributes:
null or not set at all), the event is never triggered.If the date occurred in the past, the event is triggered immediately.
Timer Start Event Notation

An Escalation Start Event starts only an inline event subprocess and produces a token when an Escalation object which it can consume appears in its parent process or subprocess instance: when designing, you can insert it either into a process which is used by a Reusable Subprocess activity or a Subprocess: both must be inline event subprocesses. In other than the Inline Event Sub-Process, the event is ignored.

Escalation Start Event Attributes
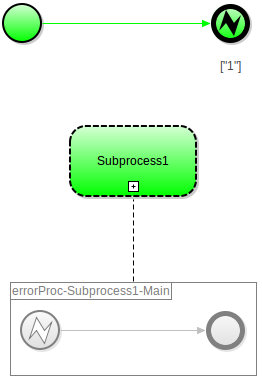
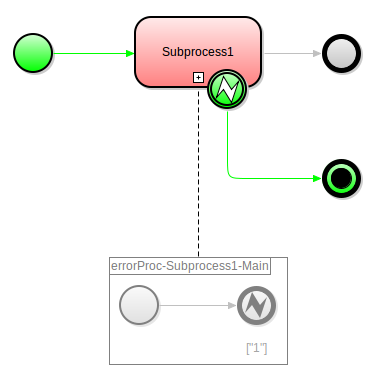
An Error Start Event triggers its flow when it receives an Error object. You can use it only as a start event of an Inline Event Sub-Process: When the parent of the sub-process throws an error and the error code matches a code in the Error Code Filter of the Error Start Event, the event creates the context of the inline event sub-process and produces a token. The Error Code Filter is evaluated at the moment when the error event is received (An Error is thrown either by the system automatically when something goes wrong, or you can throw an Error with the error() call).
The parent can be either a process instance or a sub-process instance if that the sub-process is nested in another sub-process.
In other than an Inline Event Sub-Process, the event is ignored.

An intermediate event process element handles a predictable event that can occur during workflow execution, such as, an error, timeout, breached condition, etc. When such event occurs, the event produces a token, which takes the outgoing flow of the event.
The scope the events listen to is defined by where they are placed:
on the boundary of an Activity: If the activity is Alive and the event occurs, the outgoing flow of the Intermediate Event is taken.
Note: If a boundary event is attached to a multi-instance Activity, all the instances of the Activity are interrupted when the Event is triggered.
When the Intermediate Event on an activity is triggered, the activity can either continue or terminate. This depends on the interruptibility property of the Intermediate Event:


A Timer Intermediate Event delays a workflow. The delay is defined by its date and period attributes. The interpretation of the attributes depends on where the event is placed:
Note: A Timer Intermediate Event in a workflow cannot be the target element of a Sequence Flow leaving a Gateway.


An Error Intermediate Event serves to define a workflow that is taken after an Activity produces an error: it explicitly produces an error or it ends with an Error End Event.
The element is placed on boundaries of Activities, that is, Tasks or Sub-Process. An Activity can have multiple Error Intermediate Events attached to its boundary.
An Error Intermediate Event can define a set of errors it may consume. The errors are identified by their error code. Once the event catches one of the error codes, its outgoing Flow is taken. If no error code is specified (null), the Error Intermediate Event catches any Error produced in its child contexts unless it is processed by other Error Intermediate Event, which explicitly specifies the error code.
If there are several Error Intermediate Events attached to an Activity, the Error is caught and processed by the Error Intermediate Event with the priority depending on the way its error codes are defined:


Error Code Filter defines the filter that returns the expected errors (only error events from the Error reference that meet the filter criterion trigger the event).
If no filter is defined of returns null, the event catches all errors.
A Cancel Intermediate Event is an event that handles a Cancel End Event with the aim to cancel the actions of a Transaction Sub-Process.
Hence, it can be attached only to a boundary of a Transaction Sub-Process that contains a Cancel End Event. When the Sub-Process finishes with the Cancel End Event, the outgoing flow of the Cancel Intermediate Event attached to its boundary is taken.


A Conditional Intermediate Event is an intermediate event which checks a particular condition and is triggered when the condition becomes true:
Note: There can be one or multiple Conditional Intermediate Events attached to one Activity.
true.

A Throw Signal Intermediate Event produces a Signal that can be caught by Start Signal Events and Signal Intermediate Events.
It can be used only as a workflow element with one incoming and one outgoing Flow.
When reached during execution, it sends the defined signal to the target model instances:
If no model instance is defined, the Signal is sent to its own model instance.
The Throw Signal Intermediate Event has to define the signal and the target model instances:


Note: You can throw a signal also with the
sendSignalfunction from the Standard Library.
A Catch Signal Intermediate Event is triggered when it catches a Signal. Subsequently it produces a token which takes its outgoing Flow.
It can be either attached to a boundary of an Activity or used as a workflow element with one incoming and one outgoing Normal Flow. When active it waits until it has receives a Signal.
It can define a filter for the signals it accepts; if the received signal does not meet the defined filter criteria, it does not send a token.
The Catch Signal Intermediate Event cannot handle Signals of type Reference, Goal, Plan, or ModelInstance. Catching such signals causes a runtime exception.
Catch Signal Intermediate Event defines:


A Throw Escalation Intermediate Event is an Event which sends an Escalation object when triggered.
It can be used only as a workflow object with one incoming and one outgoing flow. When reached during execution, it sends the defined Escalation object, which is propagated throughout its context and up to higher contexts either until consumed by a Start Escalation Event or a Catch Escalation Intermediate Event or until no higher context is available.
Throw Escalation Intermediate Event Attributes
Important: It is not possible to filter according to information in payload. You can use only the escalation code.
A Catch Escalation Intermediate Event is a boundary intermediate event that catches and consumes an Escalation object that was thrown in its Activity and meets the filter criterion, and produces a token. It can be used only as a boundary element on an Activity and with an outgoing Normal Flow.
The event is active while the Activity is active. When the Escalation object is thrown in the Activity or its child contexts, the boundary Catch Escalation Intermediate Event consumes the Escalation object and produces a token which takes its outgoing Flow. Note that just like other boundary Intermediate Events, it can be non-interrupting or interrupting.
Catch Escalation Intermediate Event must define a reference object, where the object is stored. It can optionally define a filter definition: if the received Escalation object does not meet the filter criteria, it is ignored.
Catch Escalation Intermediate Event Notation


Catch Escalation Intermediate Event Attributes
An End Event ends a workflow (consumes a token).
A workflow has one or multiple End Events and one or multiple Sequence Flows can enter an End Event. No outgoing Flow is allowed.
There are multiple types of End Events, which differ by the actions they perform when an execution flow enters the end events, that is, how they behave when they consume a token.
A Simple End Event is the basic end Event type which consumes the incoming token; other tokens in the workflow remain uninfluenced. The particular workflow is finished successfully if it does not contain any other tokens.
Simple End Event Notation

When a workflow reaches a Terminate End Event, all tokens in the given context and its subcontexts and the execution ends successfully: when a token reaches a Terminate End Event, any tokens in the given workflow and any sub-workflows are discarded.
For example, let's assume process A with subprocess B and subprocess C. Subprocess B finishes with a terminate end event has a subprocess BB. On runtime, subprocess B finishes with a terminate end event: As a result, any tokens in subprocess B and subprocess BB are discarded. Tokens in subprocess C and process A continue their flow unaltered.
Terminate End Event Notation

A Error End Event is an end event that implement error handling on a workflow end. The actions when triggered depend on the type of the parent namespace of the End Event. When a token enter an Error End Event, enters an Error End Event the following happens:
The End Event generates an error with the respective Error Code (see Error) and the workflow is finished. The error is distributed gradually to higher namespaces and can be caught by an Error Intermediate Event contained in any parent namespace as to trigger a compensation process (see Error Intermediate Event).
Plan Models
If a Plan Model ends with an Error End Event, the Plan fails (becomes Failed).
BPMN-based Processes
If a BPMN-based Process instance finishes with an Error End Event, the last transaction is rolled back and an exception is created.


A Cancel End Event is a special End Event which ends a Transaction Sub-Processes.
When a token enters a Cancel End Event and the parent Transaction Sub-Process has no Cancel Intermediate Event attached, the last transaction is rolled back.
If there is a Cancel Intermediate Event attached to the parent Sub-Process, the Sub-Process execution fails (the Sub-Process becomes Interrupted) and the outgoing Flow of the attached Event is taken.
Cancel End Event Notation

When a workflow ends with a Throw Escalation End Event, the event generates an Escalation object with the respective code and the workflow finishes. The escalation is distributed gradually to higher context and can be caught by a Catch Escalation Intermediate Event or Escalation Start Event in any parent context.
Escalation End Event Notation

Note: It is not possible to filter according to information in payload. You can use only the escalation code.
A No Exit End Event is an end event that consumes a token in the workflow of an Inline Event Sub-Process without triggering the Sub-Process' outgoing Flow: no token for any outgoing Flow if present is produced but the Sub-Process execution finishes with success.
If a Process with such an event is used by a Reusable Inline Event Sub-Process which is not used as part of the workflow, that is, it does not have an outgoing Flow, the No Exit End Event behaves as a Simple End Event.
