The Message component displays validation messages of failed validators in the chosen Form location. It is useful if you do not want to display these in the components with failed validation.
The Expression component defines an expression that returns a component. The expression is evaluated when the screen context is created and cannot be recalculated later.
Reusable Form component references a form: on runtime, the form is inserted into the tree of components and becomes a part of the form tree. The form is called and resolved when the screen context is created.
Note that if you want to work with events of such injected reused form in other form components or process events from other nodes inside the reused form, you will need to explicitly allow such event distribution.
The Conditional component is a form component that defines the visibility of its child components: if the Visibility property evaluates to false and the parent component is visualized or refreshed then the child components are not displayed; the children do not exist at all. Therefore it is not possible to operate over the child components unless the Conditional component defines them as visible.
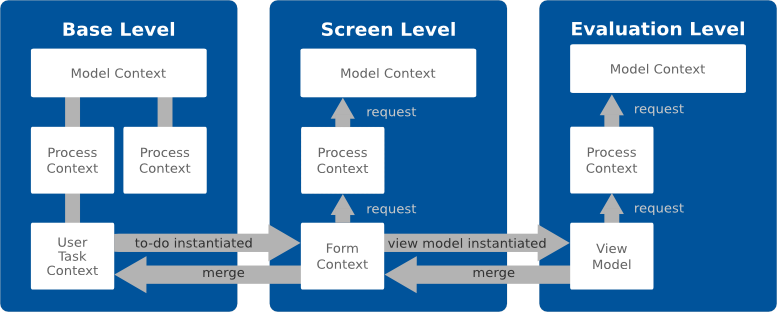
The View Model component serves to isolate changes on form data so that the changes can be applied at once or thrown away without compromising the underlying data later. The content of the view model exists in its own execution context on an evaluation level.
This is helpful, for example, when creating pop-ups: the user enters data into the popup without influencing the data in the rest of the form.
A View Model creates a new context on a higher evaluation level which overlays the current level:
Note that there might be multiple evaluation contexts on the same evaluation context level.
You can either apply the changes to the context in the underlying level or discard them. The level to which the changes are applied is defined by the merge type of the view model:
MergeType.oneLevel: the view model context is merged into the immediate underlying levelMergeType.screenLevel: the view model context is merged into the screen levelFor a view model use case, refer to Pop-up with Apply and Cancel Buttons.
To isolate transient component data use the View Model component: The component provides a "commit mechanism" by creating a context on another evaluation level. A context on an evaluation level overlays the original context so the components inside the View Model work with data in their own space. You can use a view model, for example, to implement a cancel action when editing data: the user will edit the data in the View Model and the view model will be discarded or merged on a button click.
Generally you will proceed as follows:
Alternatively, you can call the merge() and clear() functions from the handle expression.
See Pop-up with Save and Cancel Buttons for example usage.
For example, let us assume the form below.
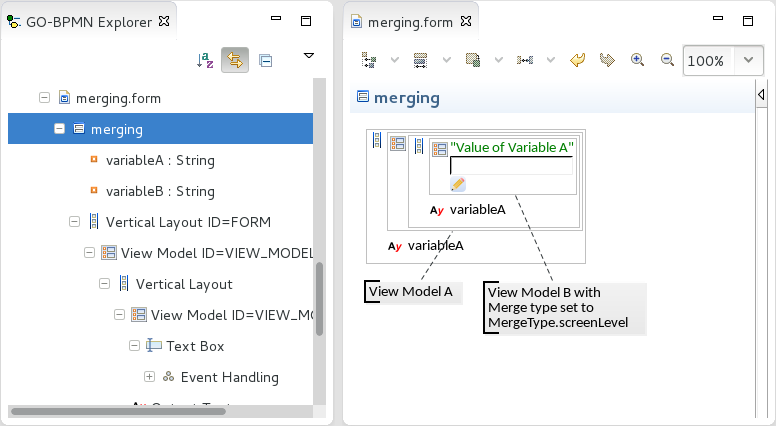
MergeType.screenLeveltrue.On runtime, if you change the variable A value in the text box, the value will be merged to the screen context via the underlying evaluation level: hence also the context in of View Model A will have the change reflected and the displayed value will be updated.
For a view model use case, refer to Pop-up with Apply and Cancel Buttons.
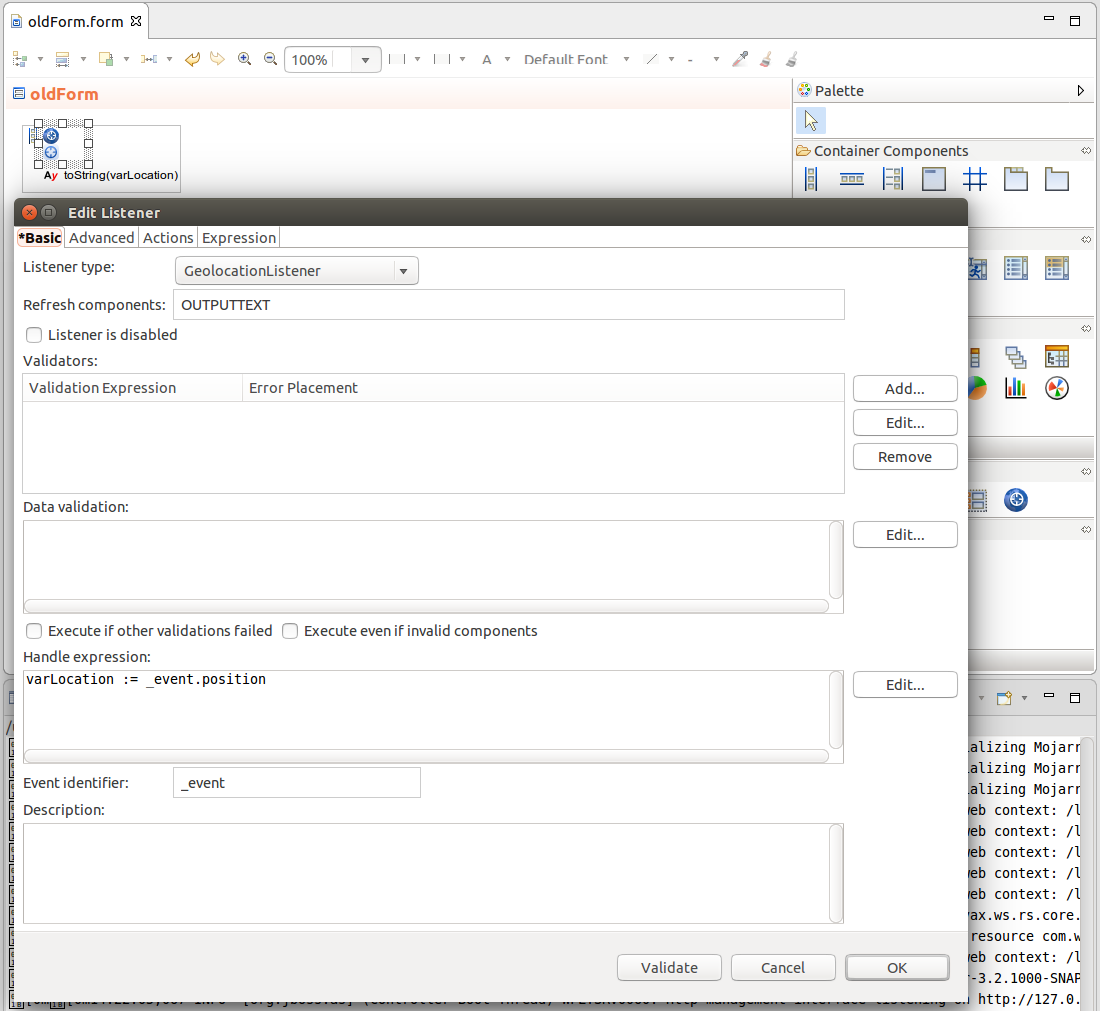
The Geolocator component serves to acquire user's location. The location is detected on initialization and every component refresh. Note the component is not rendered in a form and is intended to provide input data for other components such as the map component.
The location is acquired either from the Wi-Fi or BTS location with accuracy from 300 to 3.000 meters, or from GPS with accuracy from 1 to 10 meters.
Note: When a form with a Geolocator component is rendered, the browser asks the user whether he wants to enable the locating.
It produces events of the following types:
Note that as of the time of writing, Firefox version 24 and later do not support geolocation.
The Geolocator component has the following properties:
false the location is not detected on component refresh; this feature allows the user to disable the location detection, for example, via an action button.)ui::components.datatypes)To acquire location of the user in your form, do the following: