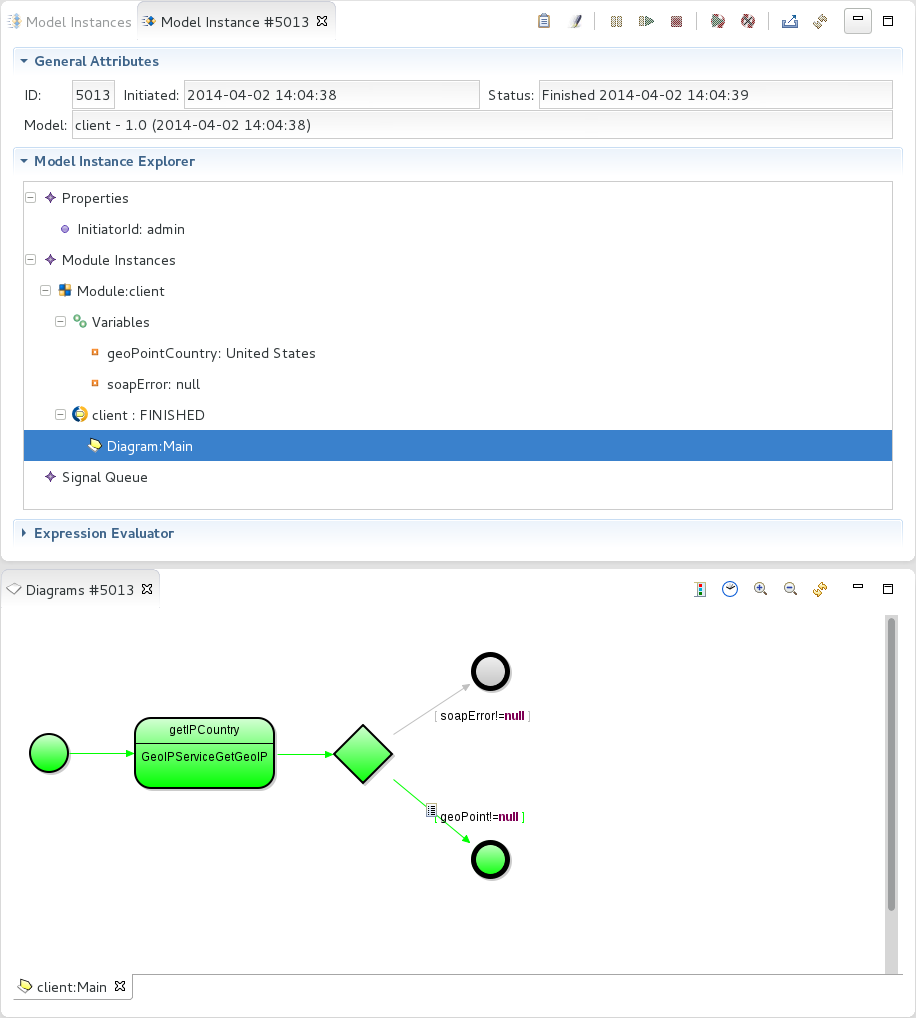
As part of your models, you can design processes that act as web-service servers or clients: The procedures differ slightly depending on whether you are creating a SOAP client or server,or a REST client or server.
You can create a process that will act as a RESTful Web Service server or client using dedicated task types:
The RESTful Web Services are implemented as required by JAX-RS: Java TM API for RESTful Web Services version 2.0 Final Release.
To create a Process that will handle REST requests, you need to create a definition and generate task types based on the definition. The task types will then serve to design the Process.
To create a REST web service server process, do the following:
error record for data sent to the client as an error
If you plan to use JSON as content type, make sure the properties of the records are only of the following types:
Path Template: template of the URL path of the service
Define the Path Template with any path variables you want to use: the variables will be added to the Path Variables table below automatically. The template supports path variables, such as, {itemID}, and regular expressions. The REST server URL is then resolved as <LSPS_Server_URL>/lsps-ws/rest/<Path_Template> and path variables are accessible as parameters of the waitRestRequest task.
The system generates the following task types:
waits until it receives a web service request from client: it accepts a request if the path of the request matches its path template. If there are several tasks waiting for a request then the task with a more precise path template handles the request. Once a task accepts the request, it finishes, and the process instance execution proceeds.
The waitRestRequest task defines the following parameters:
requestId: ID of the call
The ID is used by the response tasks to identify the call; the value is generated by the LSPS Server.
sends a response to the request with the request ID defined by its parameter.
The task defines the following parameters:
sends a fault message to the client when the received request call is evaluated as incorrect or fails.
The task defines the following parameters:
Consider global variables for the input, output, and error data types that will hold the data during the web service invocation.
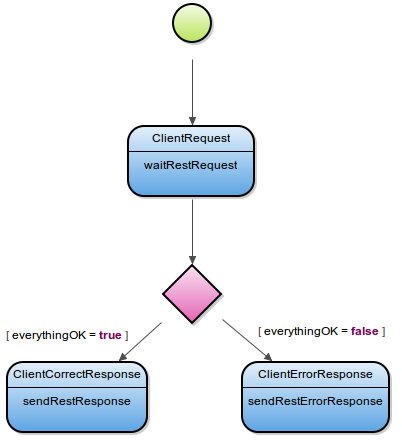
Important: If the timeout period elapses and the server has not sent any response, the server sends a timeout response to the client. The default time out is set to 10 seconds.
To create a Process that will serve as a REST client, use in the workflow the HttpCall task type or use your own task type.
Make sure to define all required parameters of the task.
Example GET HTTPCall task parameters
httpMethod /* String */ -> "GET",
url /* String */ -> "http://localhost.com:9500/3_2/section/_search",
request /* Object */ -> "{""query"":{""term"":{""title"":""model""}}}",
requestContentType /* String */ -> "application/json",
isSynchronous /* Boolean */ -> true
//equivalent to:
//curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X GET
//http://localhost.com:9500/3_2/section/_search
//-d '{"query":{"term":{"title":"model"}}}
Example POST HTTPCall task parameters
httpMethod /* String */ -> "POST",
url /* String */ -> "http://localhost:8080/lsps-ws/rest/client/123",
request /* Object */ -> convertToJson(new Input(int -> 333)),
requestContentType /* String */ -> "application/json" //"application/xml",
response /* Reference<String> */ -> &response,
responseCode /* Reference<Integer> */ -> &responseCode,
login /* String */ -> "admin",
password /* String */ -> "admin",
readTimeout /* Integer: timeout in ms */ -> 9999,
requestHeaders /* Map<String,String> */ -> [ "Accept" -> "application/json"],
responseHeaders /* Reference<Map<String,String>> */ -> ,
isSynchronous /* Boolean */ -> false
To implement a process that will serve as a SOAP server or client, you need to create the resources that represent the web service operations and design the web-service process.
You will generate Task types that implement the web service communication and will act either as a Web Service Server or a Web Service Client):
To design a process that will serve as a SOAP web-service server, you need to:
Depending on whether you have the WSDL file for the service, you will need to do the following:
You can check and manage Model instances that are serving a web service call in the Web Services view in the Management perspective or Web Management Console.
To generate task types and design a process acting as a SOAP web-service server without a WSDL, do the following:
Create the data types for the server.
All the data structures must be defined as Records even if they contain only one field of a primitive type.
Check the XML mapping of the records, their fields, and relationships on the XML Mapping tab of Properties. The mapping will be applied in the XSD, WSDL files of the service, and potentially during any XML parsing to the Records. Generally, the default mapping should work fine.
To exclude a relationship direction from the XSD schema of your server, mark the relationship direction as XML Transient: in the Properties view of the relationship, select the Target XML Mapping or Source XML Mapping tab and select XML Transient.
Service name: name used as the service name and the task name in the generated task types
The target service URL is resolved as <LSPS_Server_URL>/lsps-ws/service/<MODULE_NAME>/<Service_Name>.
Design the server Process workflow with the generated task types:
Important: Enabling logging of XML messages can result in significant database growth. Make sure to handle such risks appropriately.
Important: Enabling logging of XML messages can result in significant database growth. Make sure to handle such risks appropriately.
Important: Enabling logging of XML messages can result in significant database growth. Make sure to handle such risks appropriately.
Important: Make sure to define the id parameters on the waitForInvoke, sendResponseToInvoke, and sendErrorToInvoke. Failing to do so might result in transaction rollback.
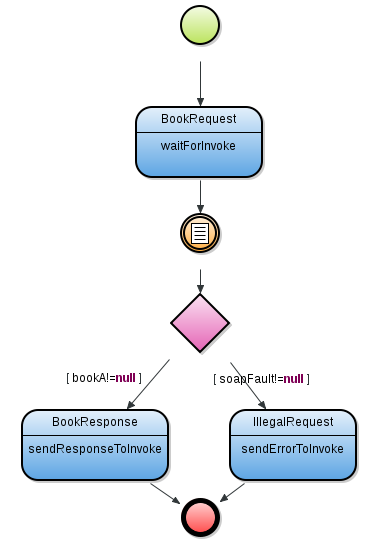
Important: If the timeout period elapses and the server has not sent any response, the server timeout response is sent to the client. The default time out is set to 10 seconds.
To generate task types and the underlying data types for web-service server from a WSDL file, do the following:
Select the optional task parameters for HTTP headers.
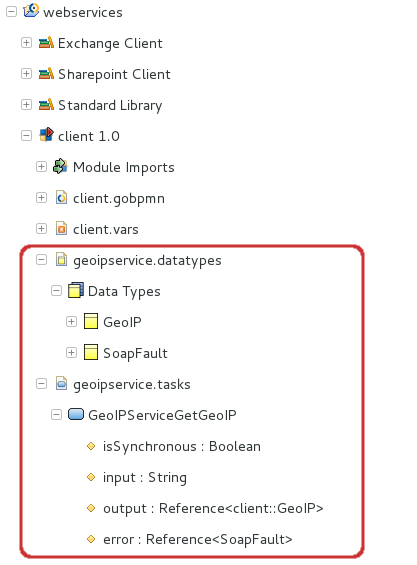
The system will create a copy of the WSDL in the Module and create the respective Records and task types. Consider storing input, output, and error data types that will hold the data during the web service invocation, in global variables.
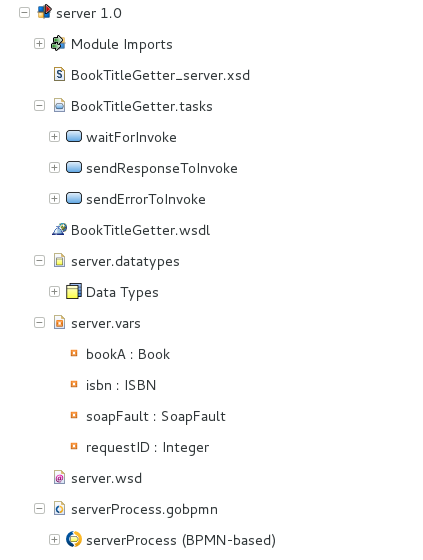

To design a Process that acts as a web service client, you will generate artifacts based on the WSDL file of the target web service. These will include the following:
Important: Resources for a web service client can be generated only for SOAP 1.1 web services.
To create data types and task types that will constitute you web-service client process, do the following:
Get the WSDL and any other related resources.
Web service WSDL is usually available on a URL provided by the web service server.
isSynchronous: if true the web service call is synchronous
Synchronous task block the execution in the entire process until the server response is received, while asynchronous tasks allow other parts of the process instance to continue their execution (other tokens in the process continue to move); for example, parallel branches continue, while the branch with the web service client task waits for the server response.
responseSoapHeaders: list of references to variables
The variables will be filled with the received soap headers if they match any of the present headers.
endpointAddress: target webservice endpoint URL address
If null, the endpoint address from metadata is used.
logXmlMessage: database logging of messages
If true, all XML messages received by the task are logged to the database (false by default).
Note: Enabling logging of XML messages can result in significant database growth.
readTimeout: read timeout in milliseconds
After the defined time period elapses, an Error is thrown. You can handle the possible error with an Error Intermediate Event. If undefined the timeout is set to zero (0) and hence no timeout is applied (the timeout is infinite).
login: login name used to access the web service
HTTP basic authentication is used.