
When creating forms with the ui module, you typically do the following:
To create a UI form definition, do the following:
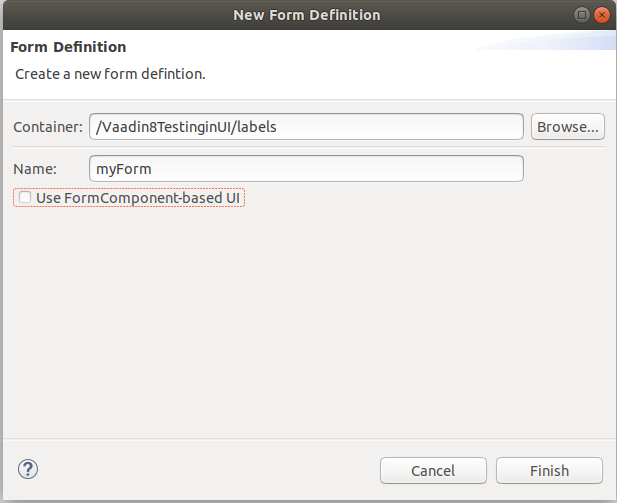
Note: If the Use FormComponent-based UI option is selected, a form based on the forms module will be created.
A forms can receive and use arguments as it parameters when it is called.
To define form parameters, do the following:
In the Outline view, right-click the form and select New > Parameter.
Alternatively, you can open the form properties in the Properties view and click Add on the Parameters tab.
When instantiating the form, the form call must pass the arguments for the parameters.
//example call that creates a parametric form:
applicationForm(user -> admin, requestedHardware -> Hardware.ssd)Forms can define form variables, which are accessible from within the form. They allow you to separate presentation data and business data: You should prefer form variables over global variables whenever possible.
Form variables are initialized when the form is displayed along with the InitEvent being fired.
To define form variables do the following:
To create the content of a form, open the form definition file (double-click it in the GO-BPMN Explorer). Then either click the required component in the palette and then click into the canvas to insert it, or right-click the canvas, go to Insert Component and select the component from the context menu.
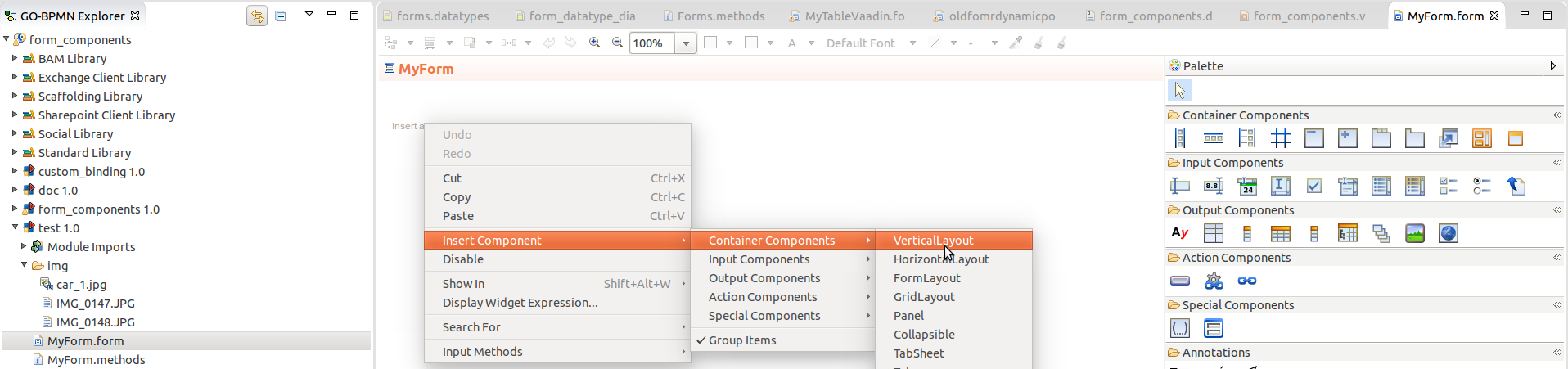
Note: You can create forms also with the dynamic-gui functions, such as createAndAdd(). However, these functions are not maintained and will not be enhanced.
Once you have created your form or while doing so, you can do the following:
You can select one or multiple form Components and wrap them with another components in the Form graphical editor.
To insert such a parent form component over another component, do the following:
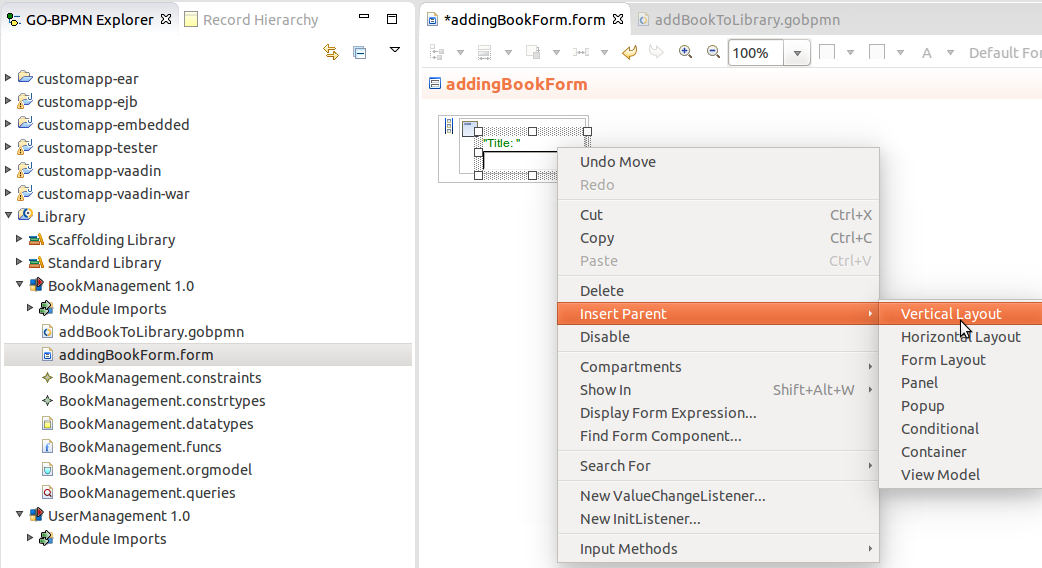
To delete a only a parent component and preserve its child components, right-click the parent component and click Shift Children Up.
Note that the option is only available if the children can be accommodated in the form after the deletion; for example, it is not possible to delete a Vertical Layout with multiple child components if it has a Panel component as its parent.
To display form preview, click the Preview button in the form editor.
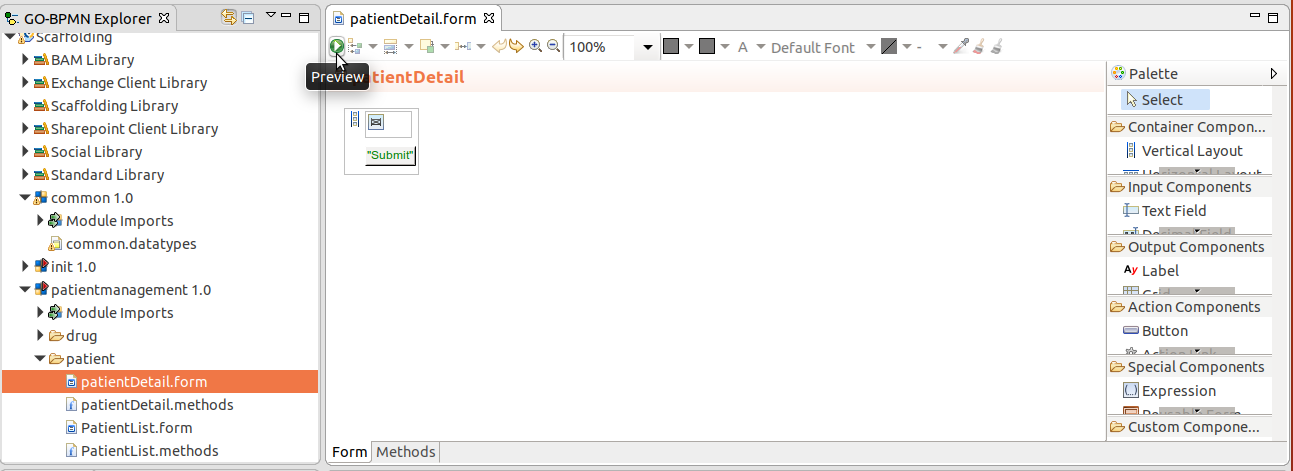
For parametric forms, add the argument to the form preview configuration.
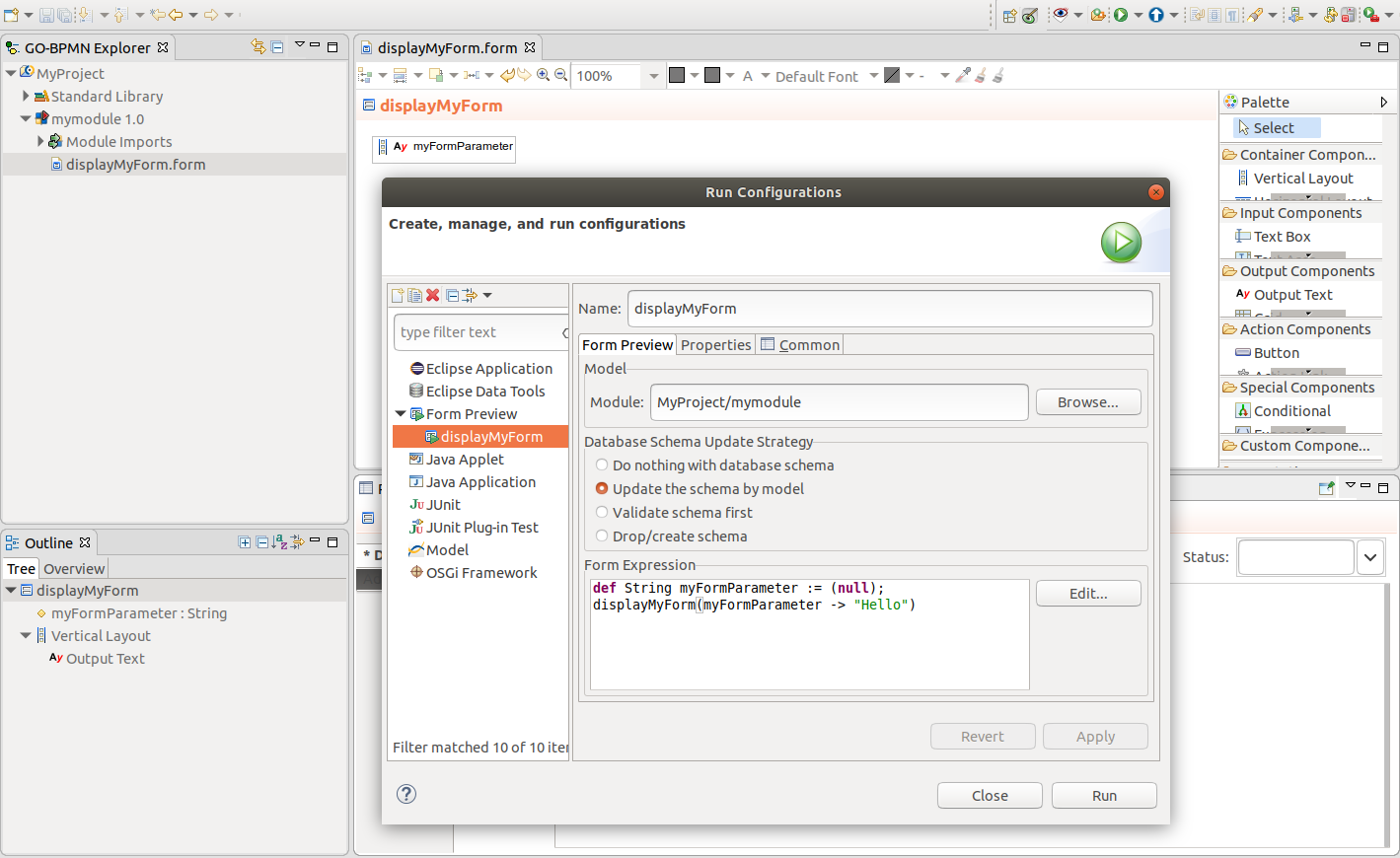
In the Management perspective, the model instances that you created as form previews are visible in the Model Instances view: to delete them, right-click anywhere into the view and click Remove All Form Preview Model Instances.
Since forms are defined as functions and their components as variables of the respective record type on the level of the Expression Language, you can display their source in the Expression editor:
If an error on a form component occurs during runtime, the server returns an error message with the modeling ID of the form component. To find the form component, do the following:
Every form component can define its context menu. The menu and its content is defined as a component property. When the user right-clicks the component, the context menu with its items is displayed. The user can then click a context menu item. On click, a MenuEvent is produced. The MenuEvent has the id of the clicked menu item as its payload so the form can define the MenuListener that will trigger the respective actions.
The context menu can be defined as static or dynamic: A static context menu is calculated only once before the form is rendered, while a dynamic context menu is recalculated on every right-click. This might cause performance issues since it could require accesses to server on every right-click.
If you define both a static and a dynamic context menu on right-click, the displayed context menu will contain the static menu items on top and the dynamic menu items below.
To define a context menu on a component, do the following:
[new MenuItem(
caption -> "Open the Detail",
htmlClass -> "contextmenu",
id -> 0,
submenu -> [new MenuItem(
caption -> "Open in a New Tab",
htmlClass -> "contextmenu",
id -> 1),
new MenuItem(
caption -> "Open in This Tab",
htmlClass -> "contextmenu",
id -> 2)
]
)
]
Define the action that should occur when the item is clicked in a MenuListener.
Example Handle expression on a MenuListener
_event.id == 1 ? (MENUITEMCLICK.content := { -> "Menu item with id 1 has been clicked." }) : nullYou can define listeners on any form component; however, every component type allows only listeners for events it can actually produce; for example, a Button component can define only an Action listener, which is fired when the user clicks a button. It cannot define a ValueChange listener since there is no value to be changed on a Button. On the other hand, a component might produce various events: A button produces just like all components an InitEvent when it is created: An Action listener on the Button will ignore the event: it catches only the events of a particular type on its component.
Note: To listen for an event on another component, you can do one of the following:
- To listen for events from child reusable forms or to listen on events from parent forms, use Container interface with public listeners and registration points.
- Produce an application event.
To create a listener on a form component:
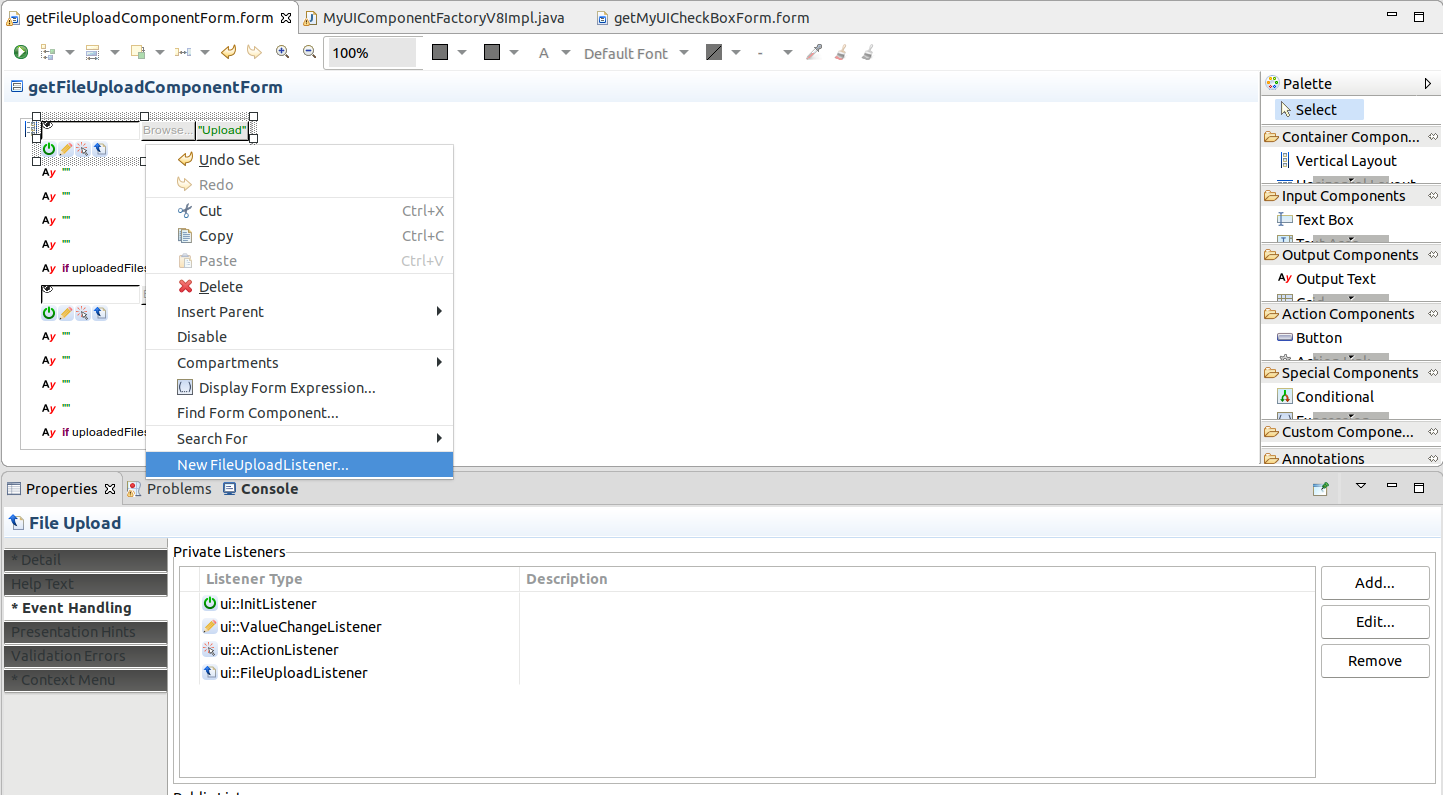
Note that the event caught by the listener is available to expressions on all tabs with the exception of the Handle expression; however, the type of the event is not recognized so you might need to cast it to its type, for example, _event.cast(InitEvent).
To disable a listener on design time, open its properties and select Listener is disabled on the Basic tab.
To exclude an event so it is not caught by the listener under certain circustances, use one of the following listener properties on the Advanced tab:
true. if ((_event as ApplicationEvent).payload as Integer) = 1 then true else false end
Note: An event might not be processed also if the validation process fails.
Sometimes you want to ignore queued events from other components, for example, in forms with multiple tabs, you want to ignore events on tabs that are not focused at the given moment, or you want to prevent validation on components while resetting the content of another component, etc.
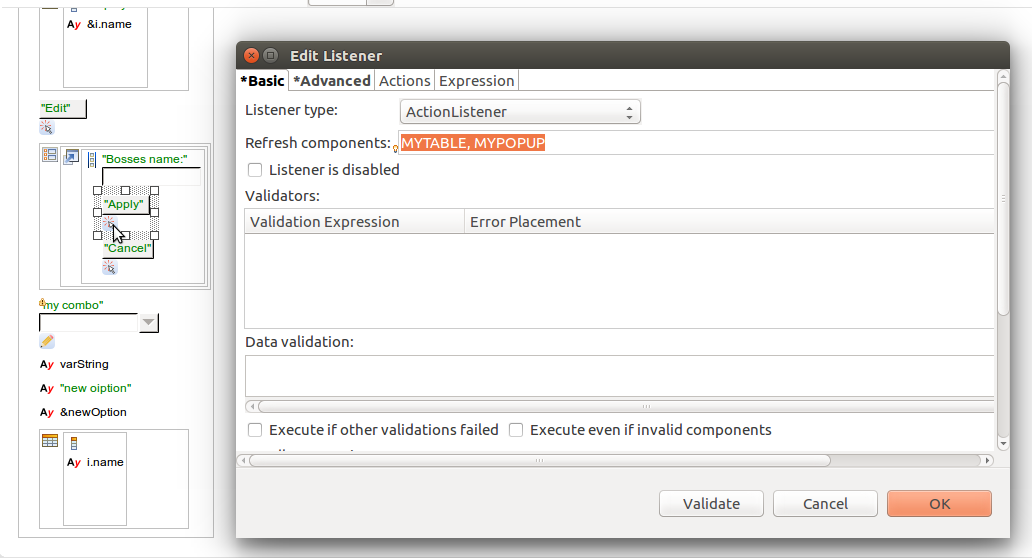
To ignore events produced by other components when a particular event is processed, set the Process component property on the Advanced tab in your listener properties:
For example, let's assume a table with column A and column B. Both columns contain input components that are not-immediate and buttons used to submit the values from the given column. When the user changes values, ValueChangeEvents from both columns are kept in the event queue. Then the user clicks the submit button in column A. The value change listener must define as its Process component only column A. If it defines as its Process component column B as well, all the ValueChangeEvents will be processed.
To refresh the content of form components, do the following:
Alternatively, you can call the refresh() function from the handle expression (for example, refresh([MYTABLE, MYPOPUP])).
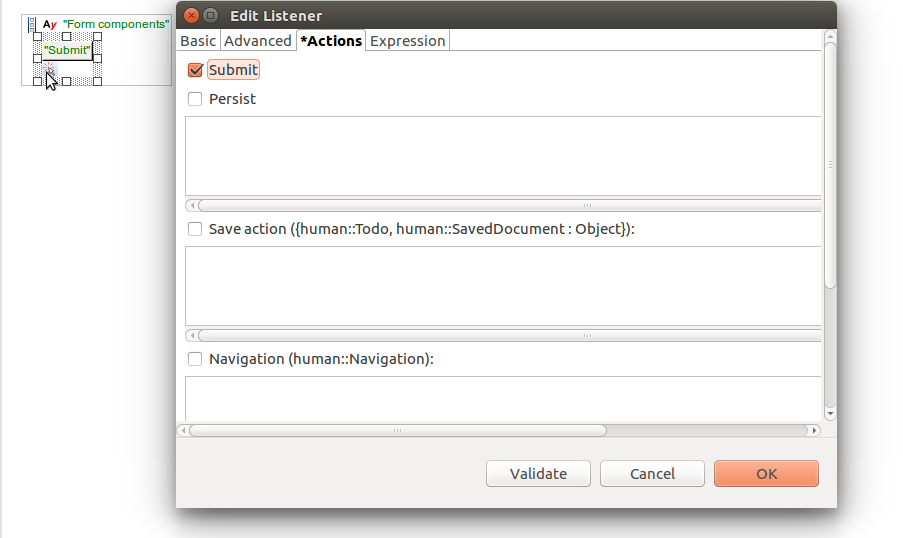
To persist the context data of a document or to-do, enable the Persist action on the Action tab of the respective listener or call the persist() function from its handle expression.
To perform an action immediately after persist, define it in the text area below the Persist checkbox,
The Persist action is performed after the merge to the screen level before the transaction is committed.
To save the state of the to-do or document for later editing, define the Save action on a listener. The action is identical to clicking the Save button on a to-do or document in the LSPS Application User Interface. Note that the save action does not persist the data, therefore make sure to activate the Persist action if required.
Note: A saved document is persisted in the system database as a SavedDocument record. If saved repeatedly, the same record is overwritten. On submit, the persisted document is removed.
To process a saved to-do or document, define the Save action closure below the Save option: it has the saved to-do or document as its input parameter.
Note that by default, Save does not preserve Column states (width and collapse state). To save these, proceed as described in Saving Column Width and Collapsed State.
To store a saved to-do or document in your own data source, define the following:
When the user submits the document or to-do, the data is saved, typically in the underlying DB via shared Records, and; in the case of documents, the model instance ceases to exist, and, in the case of to-dos, the user task finishes.
Note that the document will remain available in the list of documents since the list contains the types of documents, not their instances: Unlike To-Dos, documents availability does not depend on a Task; they are available as long as the definition of the document is on the server and their instances are created on request.
To define, when the document or to-do is submitted, do one of the following:
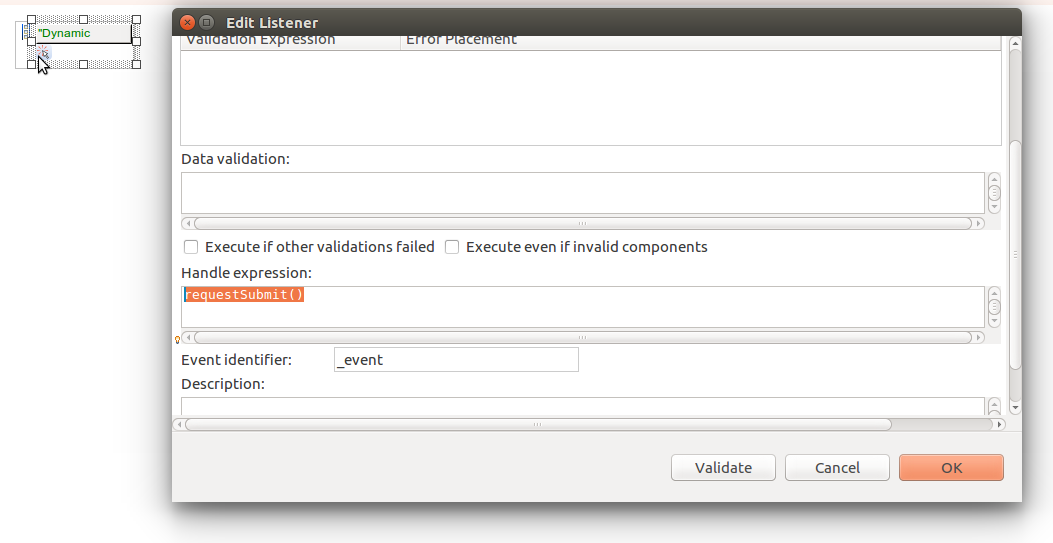
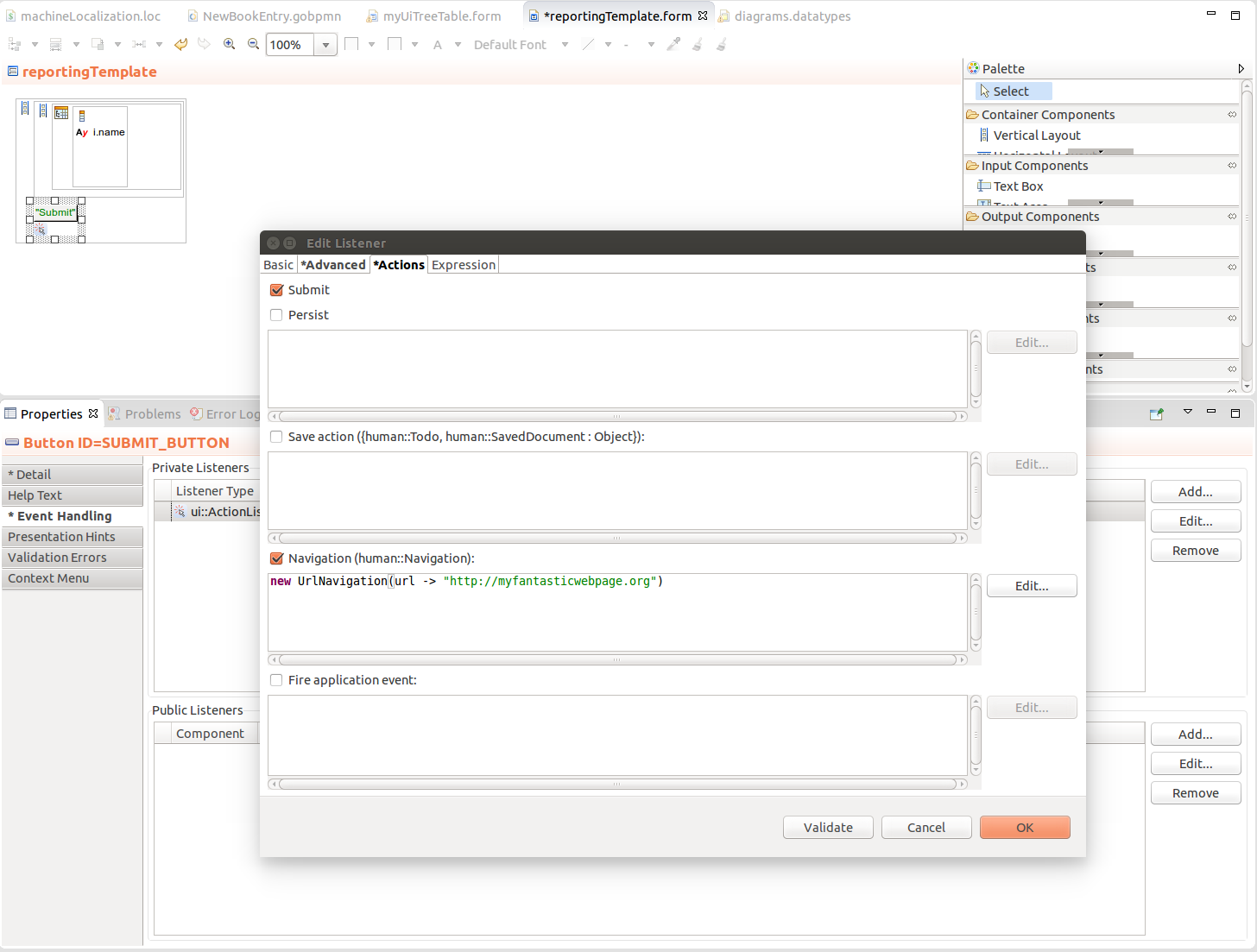
You can make a form navigate away by requesting navigation on an event action:
true.Navigation expression
The Navigation expression is evaluated right after persisting, which allows you to use the persisted data in the navigation expression. However, the action is taken only after the submit or save action is performed.
Any navigation on submit is performed in the current tab: the openNewTab parameter is ignored.
Note: You can define a Navigation also on the Document or User Task: This Navigation is used when the form is submitted and overrides the Navigation defined on the event listeners. For example, if you define a button that not only navigates but also submits the form, on submit, the document or todo navigates to the Navigation defined on the document or todo; the navigation defined on the Action tab of the event listener is ignored.
A hook executed before session timeout is define on an Action Listener of a Button or Action Link component with the simulate-click-on-session-close hint. The hint value must be set to True: right before the session timeout, the action defined on the listener is performed.
To perform an action before the browser session with the form times out, do the following:
simulate-click-on-session-close hint to the component with the value True.